Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
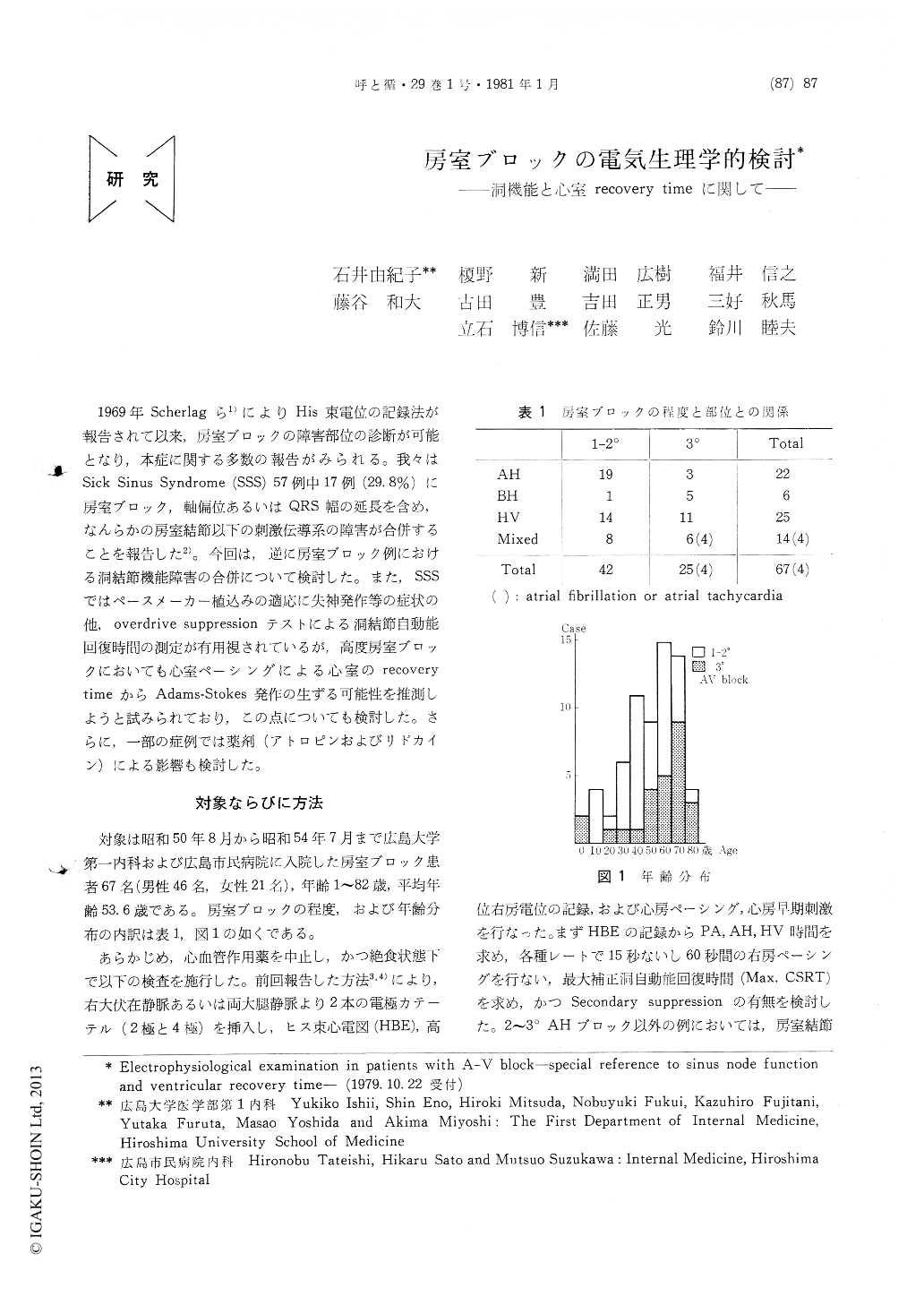
1969年Scherlagら1)によりHis束電位の記録法が報告されて以来,房室ブロックの障害部位の診断が可能となり,本症に関する多数の報告がみられる。我々はSick Sinus Syndrome (SSS)57例中17例(29.8%)に房室ブロック,軸偏位あるいはQRS幅の延長を含め,なんらかの房室結節以下の刺激伝導系の障害が合併することを報告した2)。今回は,逆に房室ブロック例における洞結節機能障害の合併について検討した。また,SSSではペースメーカー植込みの適応に失神発作等の症状の他,overdrive suppressionテストによる洞結節自動能回復時間の測定が有用視されているが,高度房室ブロックにおいても心室ペーシングによる心室のrecovery timeからAdams-Stokes発作の生ずる可能性を推測しようと試みられており,この点についても検討した。さらに,一部の症例では薬剤(アトロピンおよびリドカイン)による影響も検討した。
Electrophysiological studies were performed in 67 patients (pts) with various degree of atrio-ventricular (AV) block. 22 pts, 6 pts, 25 pts were AH, BH, HV block, respectively. 10 pts were mixed block (two lebel block), and 4 of 25 complete AV block pts had associated atrial fibrillation or atrial tachycardia (AN : 1, HV : 1, unknown : 2).
1) Detailed electrophysiologic findings of the sinus node were following : sinus node dysfunc-tion was suspected in 19/63 pts (30%). These 19 pts showed one or more following abnormali-ties. PP interval prolongation (>1200 msec, 9 pts), max. CSRT prologation (>500 msec, 17 pts), in-creased sinoatrial conduction time (>150 mec, 4 pts), secondary suppression, SA block or sinus arrest (10 pts). Atrial refractory periods were measured in 45 of 63 pts: the prolongation of ERPA(BCL)(>330 msec) and FRPA (BCL)(>360 msec) were seen were seen in 11 pts (24.4%), 10 pts (22.2%) respectively. These incidence were no significant in degree and location of AV block.
Copyright © 1981, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


