Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
- 参考文献 Reference
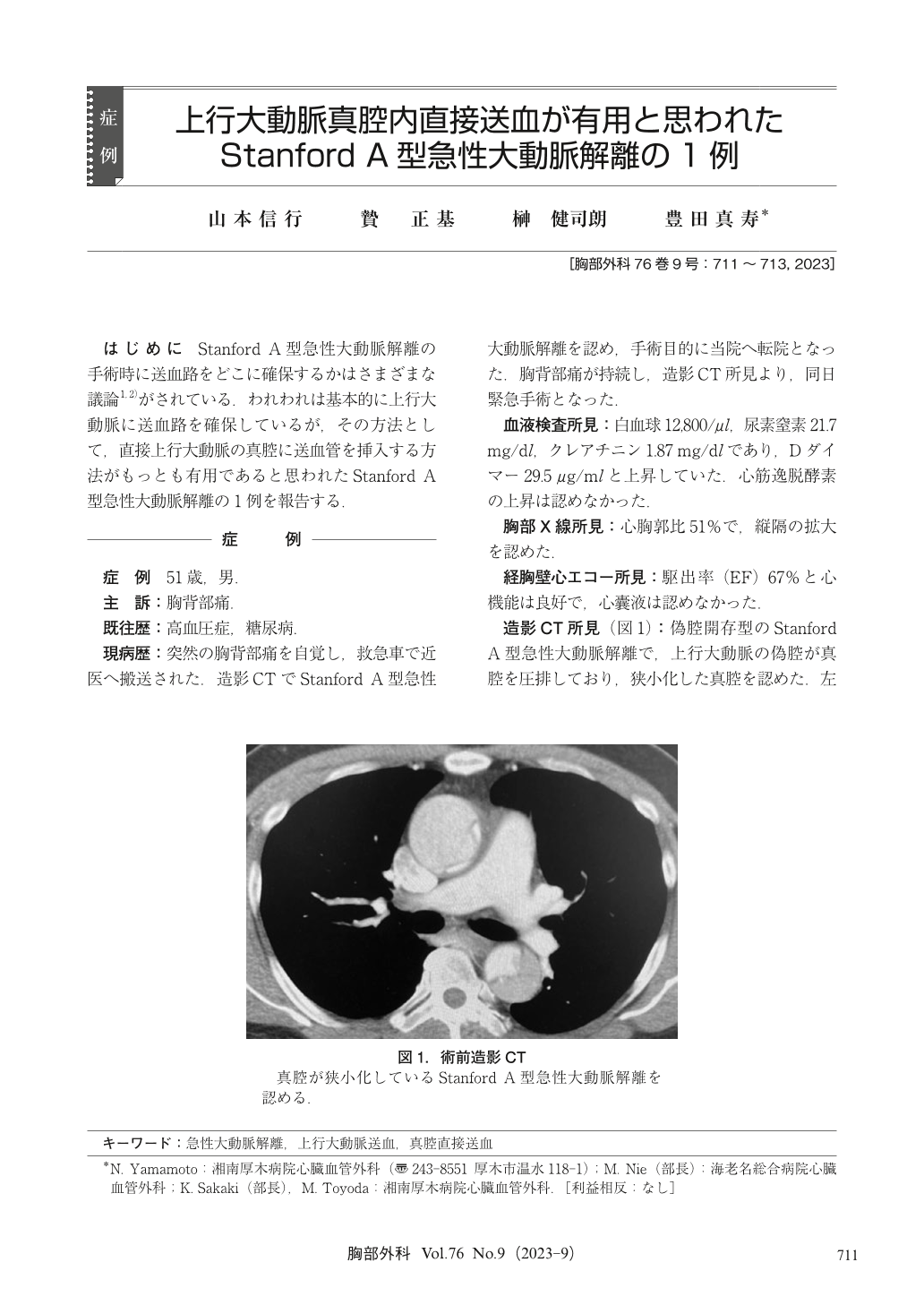
はじめに Stanford A型急性大動脈解離の手術時に送血路をどこに確保するかはさまざまな議論1,2)がされている.われわれは基本的に上行大動脈に送血路を確保しているが,その方法として,直接上行大動脈の真腔に送血管を挿入する方法がもっとも有用であると思われたStanford A型急性大動脈解離の1例を報告する.
A 51 years-old male with sudden onset of chest and back pain was referred to our hospital from another hospital. Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) revealed the presence of Stanford type A acute aortic dissection with critically narrow true lumen in the ascending aorta. Then, emergency surgery was performed. One umbilical tape tourniquet was placed around the ascending aorta. A vent tube was inserted into the main pulmonary artery. A venous drainage cannula was inserted into the right atrium. In the head-down position, pulmonary artery venting and venous drainage were initiated. As the blood puressure fell down around 40 mmHg, the ascending aorta was incised. A cannula (DLP 24 Fr) was placed in the true lumen and the aorta was snared. Cardiopulmonary bypass was established followed by selective antegrade cardioplegia, and systemic cooling. An entry was found in the ascending aorta, so ascending aorta graft replacement was performed under selective antegrade cerebral perfusion. There were no perioperative complications, and he was discharged home on 24th postoperative day. There is still remain controversies as to the optimal arterial cannulation site for cardiopulmonary bypass in patients with Stanford type A aortic dissection. We think the ascending aorta is most simply, rapidly and reliably available. In this case, direct true lumen cannulation in the ascending aorta was useful.
© Nankodo Co., Ltd., 2023