Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
- 参考文献 Reference
- サイト内被引用 Cited by
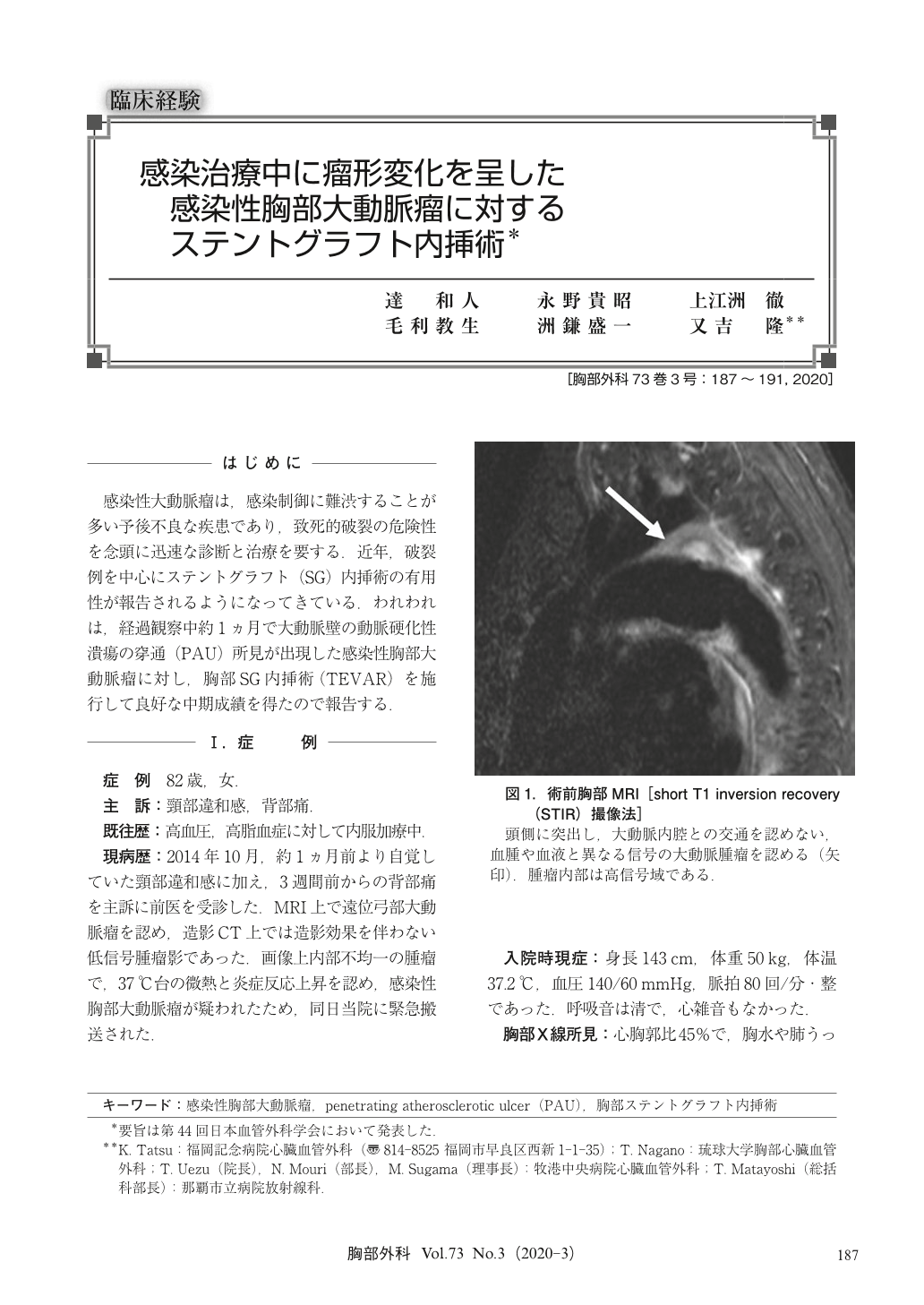
感染性大動脈瘤は,感染制御に難渋することが多い予後不良な疾患であり,致死的破裂の危険性を念頭に迅速な診断と治療を要する.近年,破裂例を中心にステントグラフト(SG)内挿術の有用性が報告されるようになってきている.われわれは,経過観察中約1ヵ月で大動脈壁の動脈硬化性潰瘍の穿通(PAU)所見が出現した感染性胸部大動脈瘤に対し,胸部SG内挿術(TEVAR)を施行して良好な中期成績を得たので報告する.
We report a successful case of infected thoracic aortic aneurysm treated by endovascular repair. An 82-year-old woman, presenting with intermittent back pain and low-grade fever, was transferred with the diagnosis of infected thoracic aortic aneurysm. High inflammatory reaction and a thickened aortic wall around the aneurysm confirmed the diagnosis. We performed infection control first because enhanced computed tomography (CT) scanning revealed aneurysm was a low-density mass, which denied aortic pseudoaneurysm or rupture. After administration of broad-spectrum antibiotics, low-grade fever was relieved and inflammatory reactions were decreased. CT performed on the 11th hospital day showed the low-density mass was decreased in size. However, CT performed on the 35th hospital day revealed penetrating atherosclerotic ulcer (PAU) into the low-density mass, which was consistent with saccular aortic aneurysm. The patient underwent thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR). Postoperative course was uneventful and she was discharged on 22nd postoperative day. Oral administration of antibiotics was continued for 6 months after discharge. Eight months after TEVAR, CT revealed disappearance of the aneurysm. The patient showed no recurrence of infection at 5 years of follow-up.
© Nankodo Co., Ltd., 2020