Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
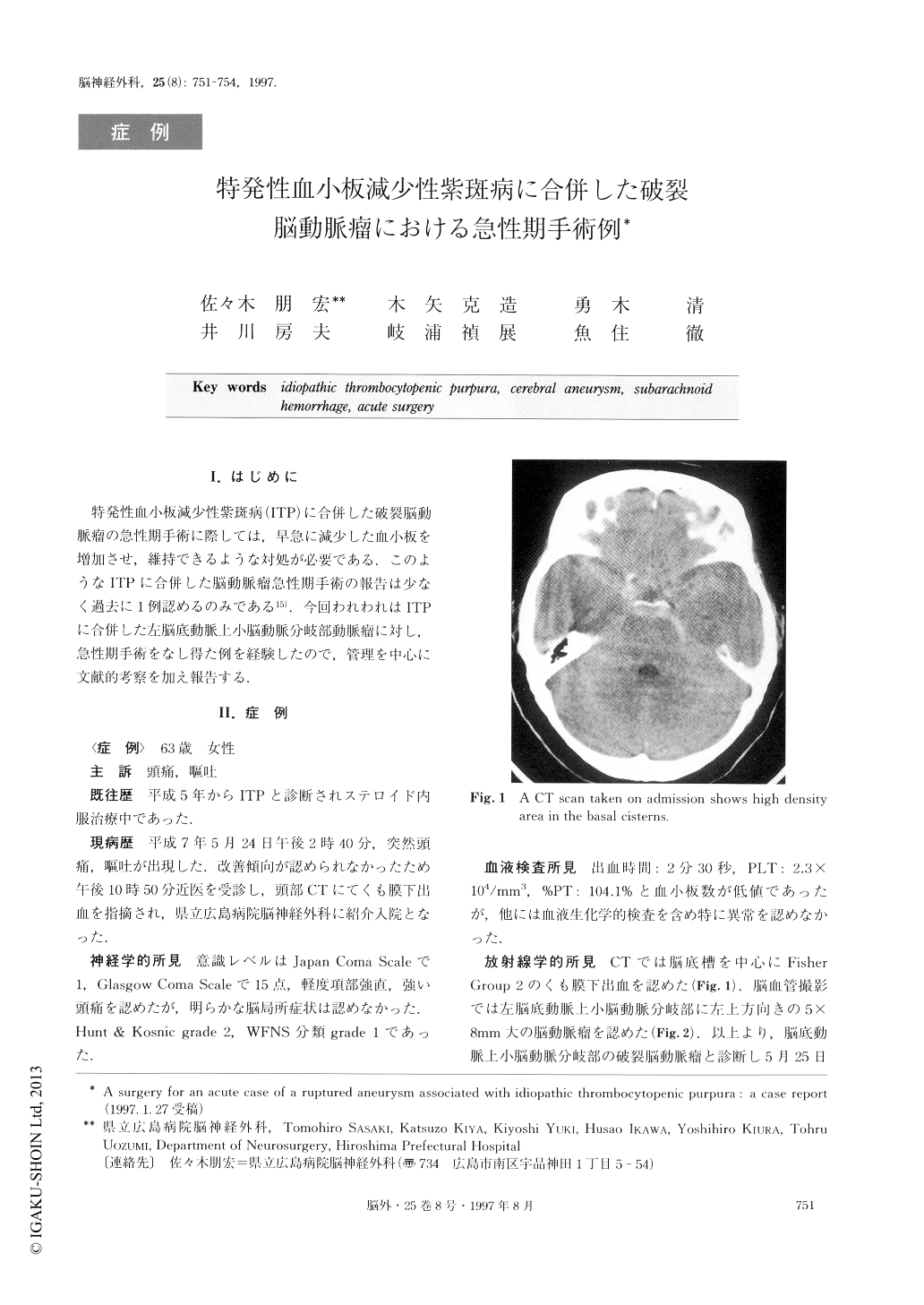
特発性血小板減少性紫斑病(ITP)に合併した破裂脳動脈瘤の急性期手術に際しては,早急に減少した血小板を増加させ,維持できるような対処が必要である.このようなITPに合併した脳動脈瘤急性期手術の報告は少なく過去に1例認めるのみである15).今回われわれはITPに合併した左脳底動脈上小脳動脈分岐部動脈瘤に対し,急性期手術をなし得た例を経験したので,管理を中心に文献的考察を加え報告する.
A surgery for an case acute of a ruptured aneurysm with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) is very rare. We encountered a case of a ruptured basilar artery (BA)-superior cerebellar artery (SCA) aneurysm associated with ITP. A successful operation was carri-ed out while the patient was in the acute stage. The pa-tient was a 63-year-old female. She has been suffering from ITP for two years, when she experienced a sud-den severe headache and vomitting on May 5, 1995. She was referred to our hospital as a case of subarach-noid hemorrhage estimated to be in group 2 according to the Fisher grade. Her neurological condition caused by the subarachnoid hemorrhage was grade 2 accord-ing to Hunt & Kosnik classification, and she was classi-fied according to WFNS as grade 1. The number of platelets was, however, 2.3×104/mm3on admission. Cerebral angiography showed the aneurysm at the bifu-rcation of BA and SCA. The administration of platelet tranfusion, betamethasone and γ-g lobulin induced an increase of the number of platelets to 8.7×104/mm3just before the operation. Neck clipping for the aneu-rysm was performed using platelet transfusion via the right pterional approach 25 hours after the onset. No tendency to bleed was recognized during the operation. The number of platelets was kept constantly at the level between 16.9×104/mm3 and 22.0×104/mm3 dur-ing the postoperative course with the administration of betamethasone. The postoperative course was good with no manifestations of delayed ischemic neurological deficits.
Copyright © 1997, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


