Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
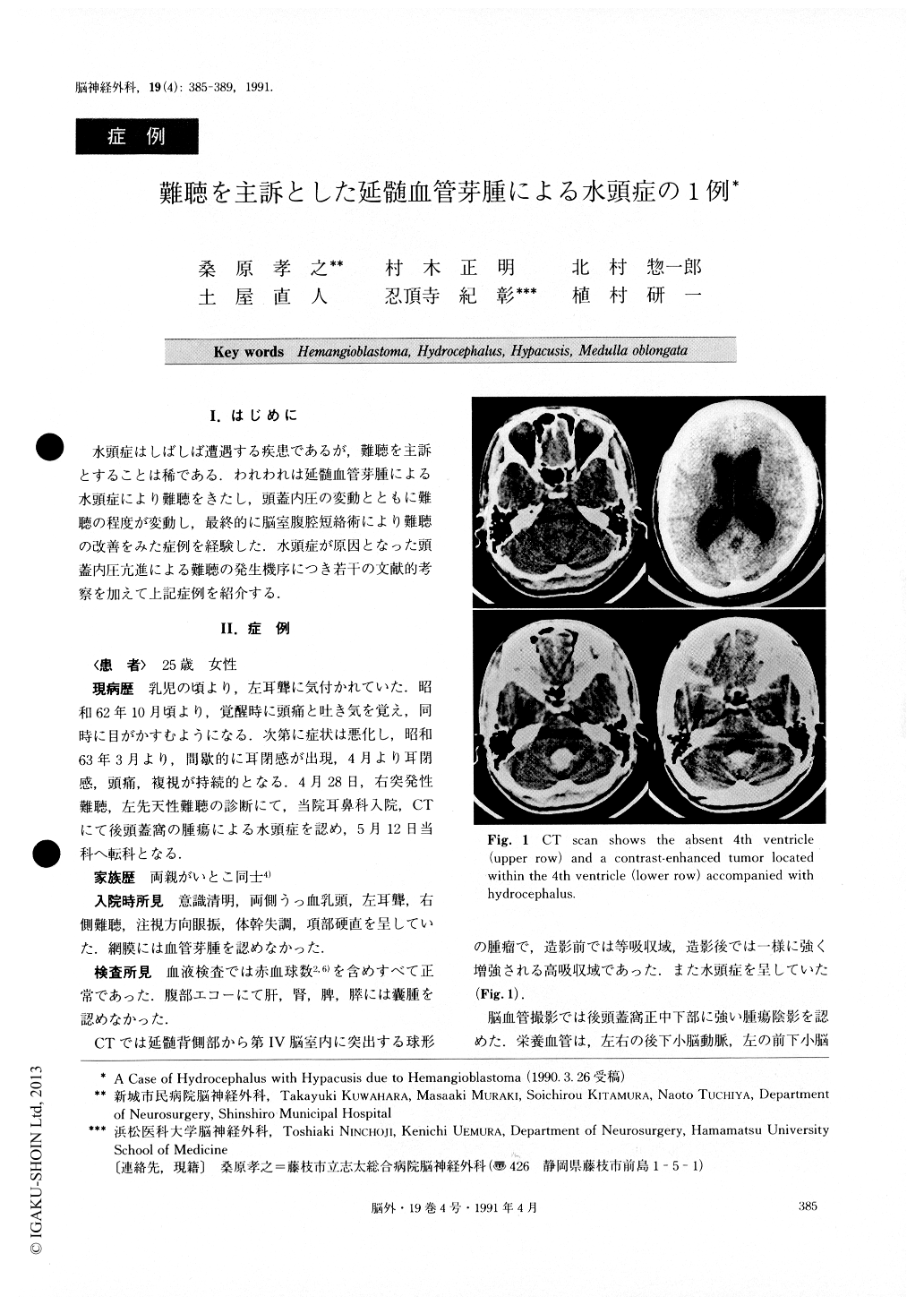
水頭症はしばしば遭遇する疾患であるが,難聴を主訴とすることは稀である.われわれは延髄血管芽腫による水頭症により難聴をきたし,頭蓋内圧の変動とともに難聴の程度が変動し,最終的に脳室腹腔短絡術により難聴の改善をみた症例を経験した.水頭症が原因となった頭蓋内圧亢進による難聴の発生機序につき若干の文献的考察を加えて上記症例を紹介する.
Abstract
A case of a brain stem hemangioblastoma with recur-rent episodes of hypacusis due to progression of hy-drocephalus is reported. The patient was a 25-year-old female, admitted to the department of otorhinolaryngo-logy with complaints of hearing difficulty, headache and blurred vision. Neuroradiological studies showed a tumor from the medulla oblongata, obliterating the IVth ventricle, and a secondary hydrocephalus. Hearing loss fluctuated as hydrocephlus progressed. Multiple V-P shunting procedures relieved episodic hypacusis. The patient remains asymptomatic at present and has re-sumed normal activity.
The mechanism of episodic hearing loss due to hy-drocephalus is thought to be due to the fact that through the ductus perilymphaticus and the ductus en-dolymphaticus, especially the former, increased in-tracranial pressure is transmitted to the inner ear. Through the ductus perilymphaticus there is com-munication between the perilymphatic space and the in-tracranial subarachnoid space. Through the ductus en-dolymphaticus there is communication with the subdu-ral space. Increased ICY effects the inner ear, It is sus-pected that, in this particular case, the progression of hydrocephalus effected the patient's hearing.
Copyright © 1991, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


