Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
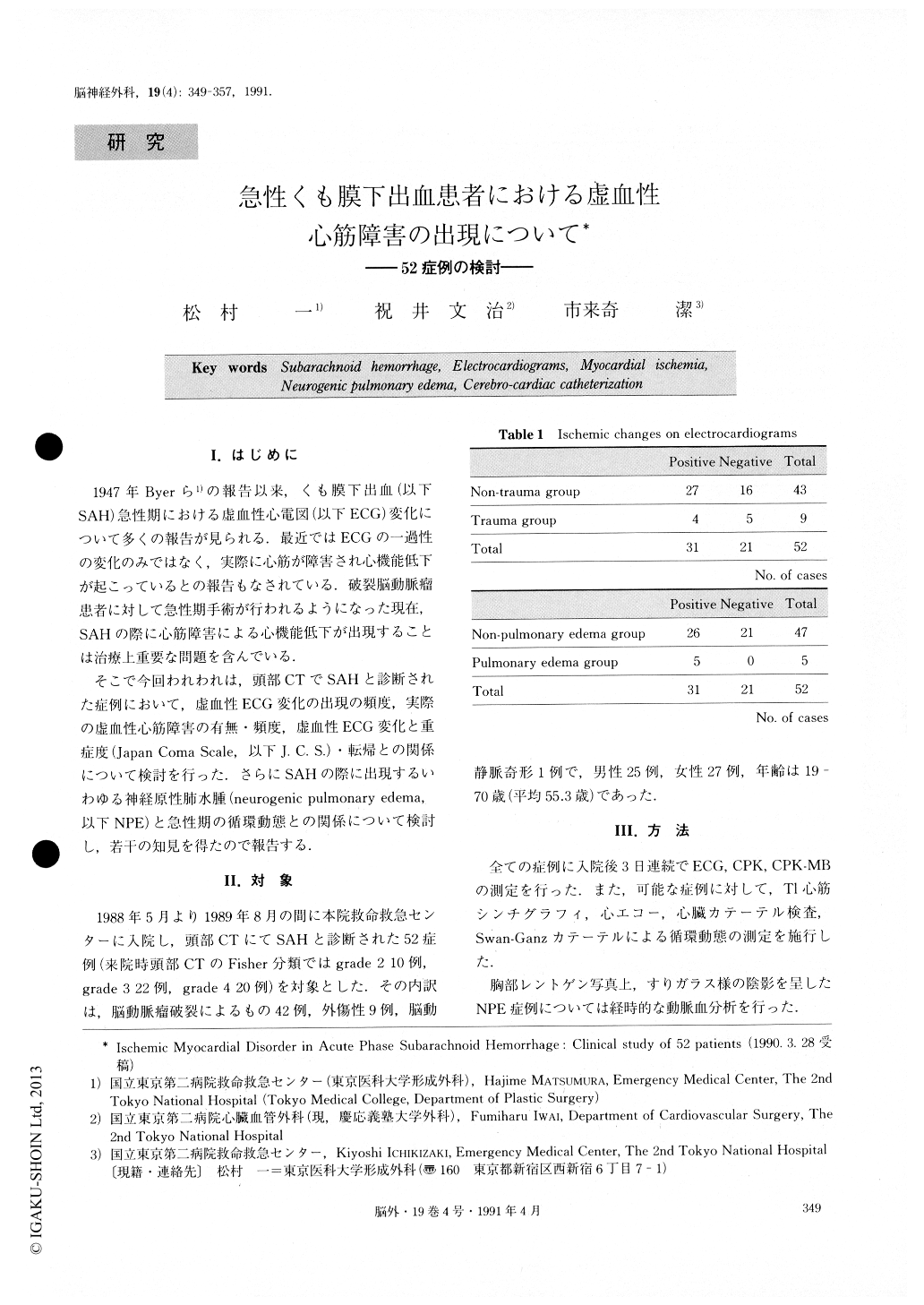
1947年Byerら1)の報告以来,くも膜下出血(以下SAH)急性期における虚血性心電図(以下ECG)変化について多くの報告が見られる.最近ではECGの一過性の変化のみではなく,実際に心筋が障害され心機能低下が起こっているとの報告もなされている.破裂脳動脈瘤患者に対して急性期手術が行われるようになった現在,SAHの際に心筋障害による心機能低下が出現することは治療上重要な問題を含んでいる.
そこで今回われわれは,頭部CTでSAHと診断された症例において,虚血性ECG変化の出現の頻度,実際の虚血性心筋障害の有無・頻度,虚血性ECG変化と重症度(Japan Coma Scale,以下J.C.S.)・転帰との関係について検討を行った.さらにSAHの際に出現するいわゆる神経原性肺水腫(neurogenic pulmonary edema,以下NPE)と急性期の循環動態との関係について検討し,若干の知見を得たので報告する.
Abstract
Fifty-two cases of acute phase subarachnoid hemor-rhage were studied by brain CT scanning to determine the presence and incidence of ischemic myocardial dis-order, the relationship between ischemic change and severity, disease prognosis, and the relationship be-tween acute phase circulatory dynamics and so-called neurogenic pulmonary edema. In all cases, ECGs were carried out and CPK-MB determined. Some of the pa-tients underwent T/ myocardial scintigraphy, echocar-diography, cardiac catheterization, as well as circula-tory dynamic investigation (by Swan-Ganz catheter) and arterial blood gas analysis. In 31 of the 52 cases (59.6%) , 3-day ECG series revealed ischemic changes. These findings were backed up by other cardiac func-tion tests, thus suggesting that myocardial ischemia was present. Results in cases undergoing cardiac catheterization revealed that the myocardial ischemic changes were not due to organic constriction of the coronary artery. Included in those cases in which ECG markedly changed and CPK-MB rose substantially were many patients for whom the prognosis was poor. Evaluation of respiratory function and circulatory dyna-mics in cases of so-called neurogenic pulmonary edema seemed to indicate decline in cardiac function owing to myocardial ischemic change. This could account for onset of symptoms. These findings support the need for adequate circulatory management in cases of acute sub-arachnoid hemorrhage with pulmonary edema and/or changes on ECG. In such cases, concurrent catheteriza-tion and cerebral angiography (cerebro-cardiac catheterization : CCC) proved effective for evaluating cardiac function and determining whether heart disease was also present.
Copyright © 1991, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


