Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
高等動物において,ホルモン,神経伝達物質,オータコイドや光,嗅物質といった細胞外の情報は,細胞膜上の特異的受容体を介して細胞内に伝えられる。
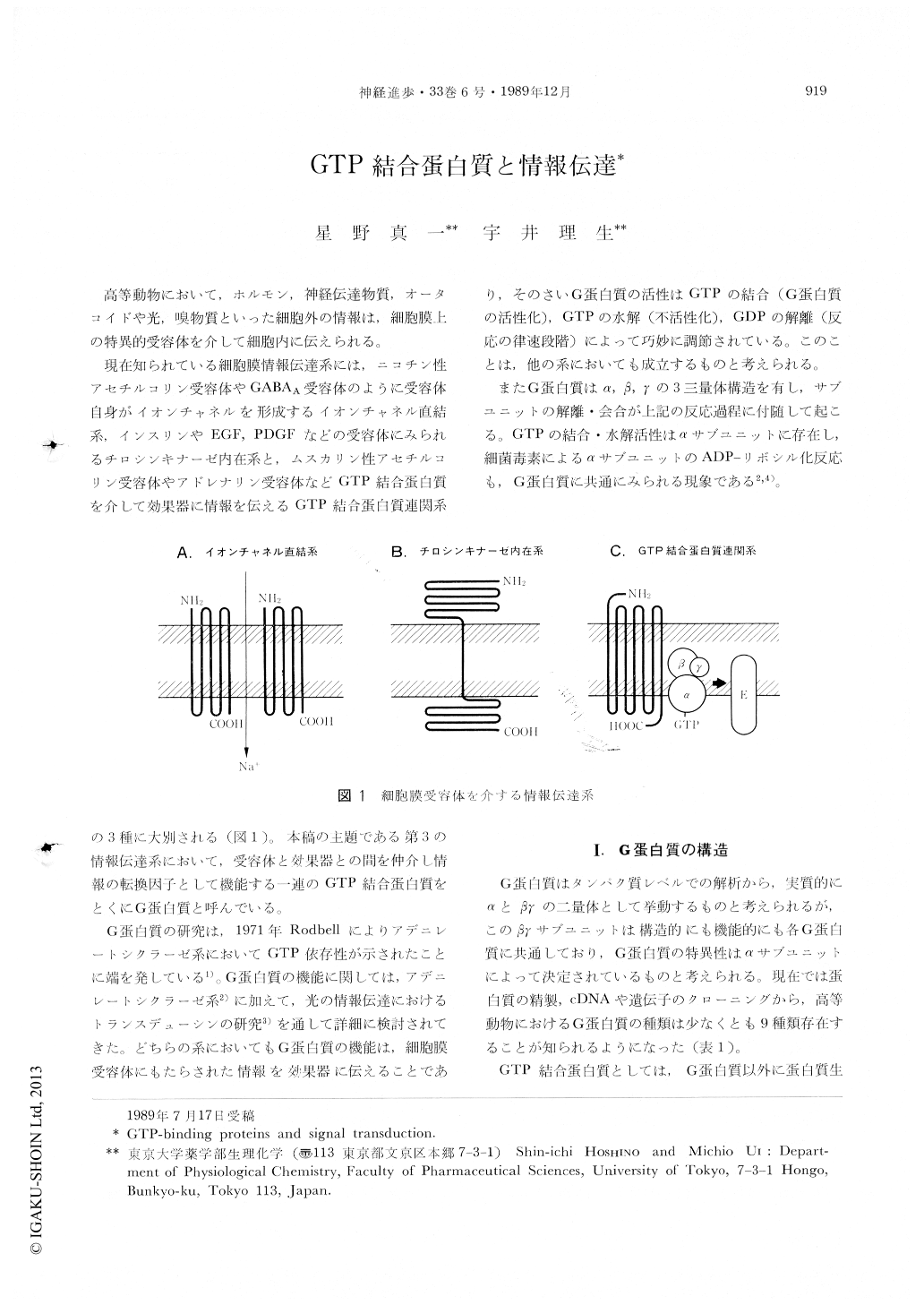
現在知られている細胞膜情報伝達系には,ニコチン性アセチルコリン受容体やGABAA受容体のように受容体自身がイオンチャネルを形成するイオンチャネル直結系,インスリンやEGF,PDGFなどの受容体にみられるチロシンキナーゼ内在系と,ムスカリン性アセチルコリン受容体やアドレナリン受容体などGTP結合蛋白質を介して効果器に情報を伝えるGTP結合蛋白質連関系の3種に大別される(図1)。本稿の主題である第3の情報伝達系において,受容体と効果器との間を仲介し情報の転換因子として機能する一連のGTP結合蛋白質をとくにG蛋白質と呼んでいる。
GTP-binding proteins are a family of membrane-bound guanine nucleotide binding proteins which play key roles in transduction of extracellular signals given to cell surface receptors to membrane effectors producing intracellular signals. The mechanism of signal transduction by the proteins in best characterized in the adenylate cyclase system and for transducin, the G protein in retina. Recent progress in molecular characterization of G proteins revealed occurrence of at least 9 distinct entities of molecule in mammals. Since most of the mammalian cells contain multiple G proteins with structural similarities, a current problem is to explain how specificity is achieved among the different proteins.
Copyright © 1989, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


