Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
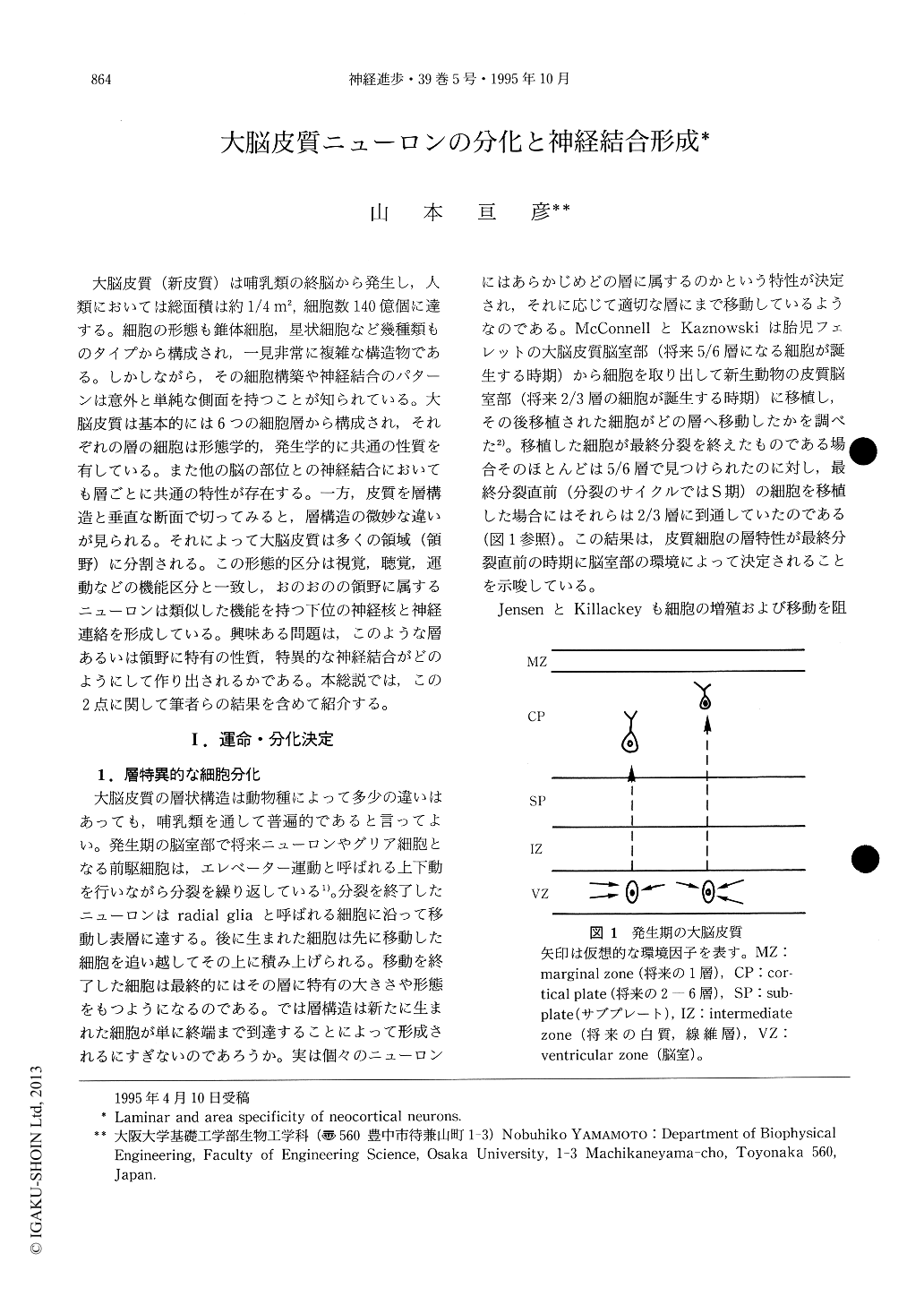
大脳皮質(新皮質)は哺乳類の終脳から発生し,人類においては総面積は約1/4㎡,細胞数140億個に達する。細胞の形態も錐体細胞,星状細胞など幾種類ものタイプから構成され,一見非常に複雑な構造物である。しかしながら,その細胞構築や神経結合のパターンは意外と単純な側面を持つことが知られている。大脳皮質は基本的には6つの細胞層から構成され,それぞれの層の細胞は形態学的,発生学的に共通の性質を有している。また他の脳の部位との神経結合においても層ごとに共通の特性が存在する。一方,皮質を層構造と垂直な断面で切ってみると,層構造の微妙な違いが見られる。それによって大脳皮質は多くの領域(領野)に分割される。この形態的区分は視覚,聴覚,運動などの機能区分と一致し,おのおのの領野に属するニューロンは類似した機能を持つ下位の神経核と神経連絡を形成している。興味ある問題は,このような層あるいは領野に特有の性質,特異的な神経結合がどのようにして作り出されるかである。本総説では,この2点に関して筆者らの結果を含めて紹介する。
The neocortex develops from the mammalian telencephalon and reaches a huge structure in human beings. The cortex is basically composed of six cell layers and devided into a lot of areas which are distinguished by laminar arrangement. According to these organizations, cortical neurons are connected with other parts of the brain. An interesting question is how cortical neurons are differentiated into lamina-and area specific cell types and how specific afferent and efferent connections are established.
Copyright © 1995, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


