Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
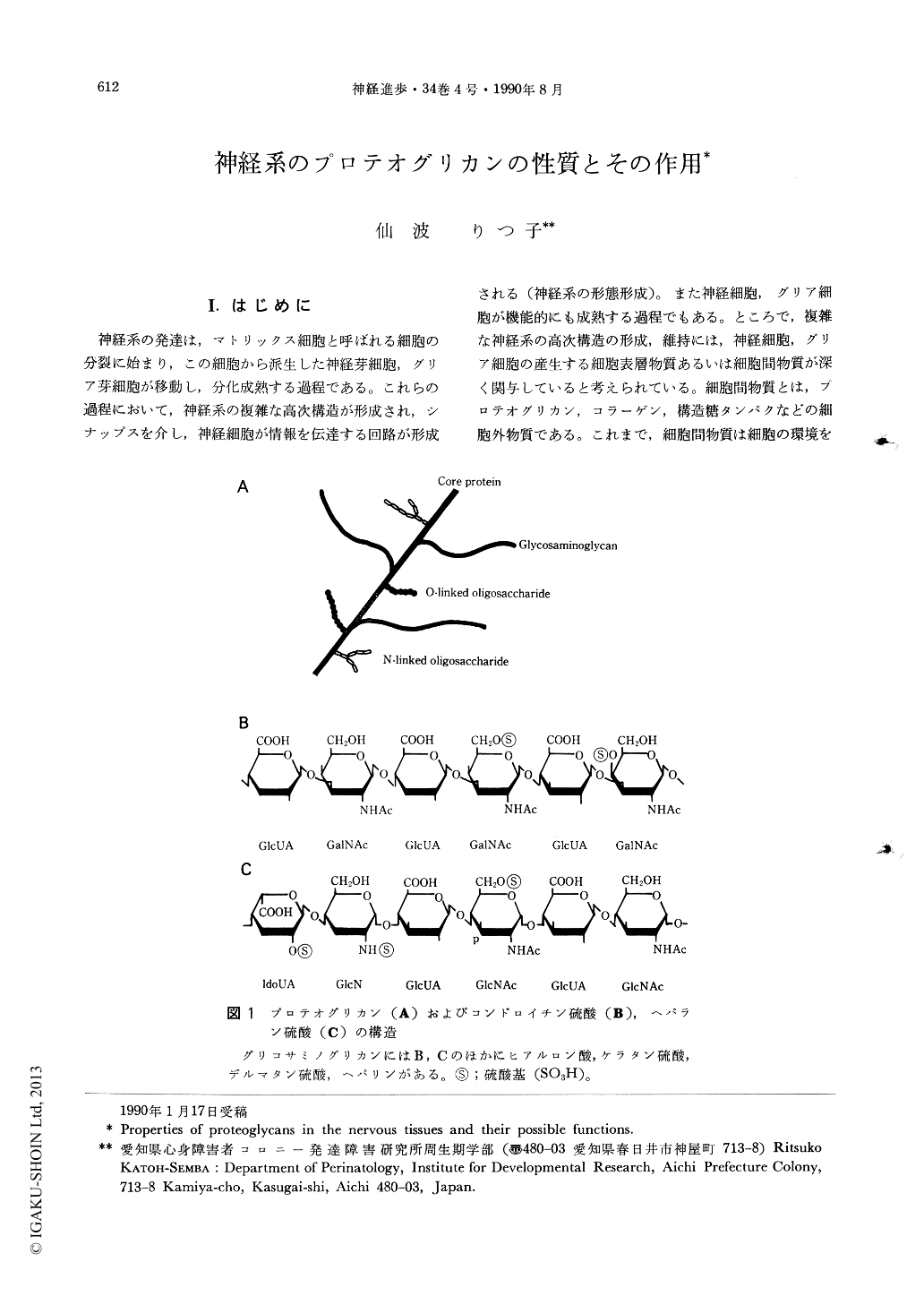
神経系の発達は,マトリックス細胞と呼ばれる細胞の分裂に始まり,この細胞から派生した神経芽細胞,グリア芽細胞が移動し,分化成熟する過程である。これらの過程において,神経系の複雑な高次構造が形成され,シナップスを介し,神経細胞が情報を伝達する回路が形成される(神経系の形態形成)。また神経細胞,グリア細胞が機能的にも成熟する過程でもある。ところで,複雑な神経系の高次構造の形成,維持には,神経細胞,グリア細胞の産生する細胞表層物質あるいは細胞間物質が深く関与していると考えられている。細胞間物質とは,プロテオグリカン,コラーゲン,構造糖タンパクなどの細胞外物質である。これまで,細胞間物質は細胞の環境を保つものと考えられていたが,近年,細胞間物質がもう少し積極的な作用,すなわち神経細胞の増殖,接着,移動,分化といった過程に直接影響を及ぼすことが示唆されるようになってきた1~4)。本稿においては,プロテオグリカンの構造,神経系のプロテオグリカンの種類に触れるとともに,神経細胞の分化にプロテオグリカンがどのように作用するかについて最近の話題を提供したい。
Proteoglycans (PGs) are one of glycoproteins that contains a core protein to which at least one glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chain and oligosaccharides are covalently bound. This simple definition encompasses a wide range of structures involving different core proteins, different classes of GAG, and different numbers and lengths of the GAG chain. Due to such complex structures, attempts at the characterization of PGs in the nervous tissues have not been fully successful yet. Recently, reports on the characterization of PGs are increasing. The purpose of this chapter is to introduce properties of PGs in the nervous tissues and their possible role in morphogenesis of the nervous system.
Copyright © 1990, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


