Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
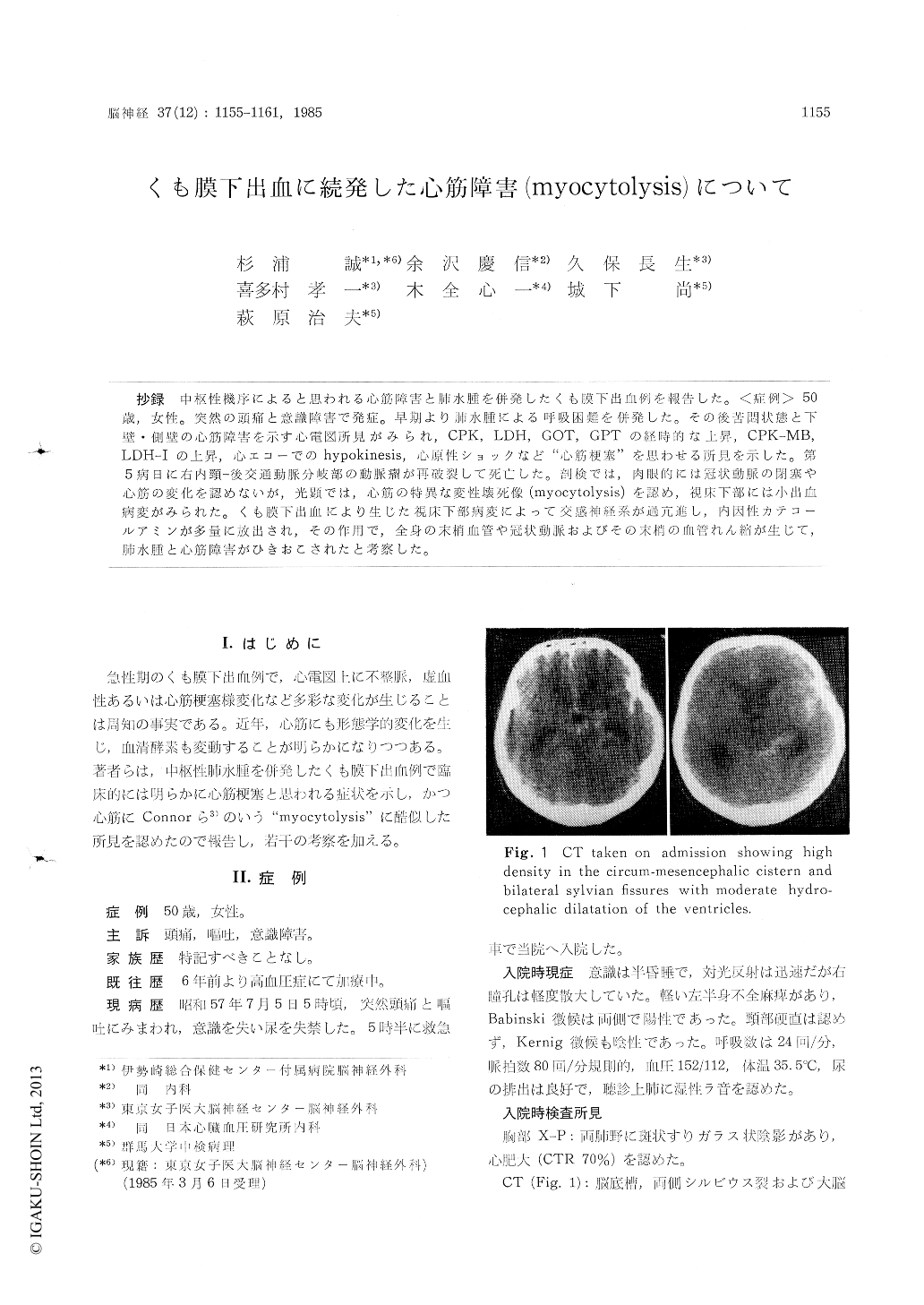
抄録 中枢性機序によると思われる心筋障害と肺水腫を併発したくも膜下出血例を報告した。<症例>50歳,女性。突然の頭痛と意識障害で発症。早期より肺水腫による呼吸困難を併発した。その後苦悶状態と下壁・側壁の心筋障害を示す心電図所見がみられ,CPK, LDH,GOT,GPTの経時的な上昇,CPK-MB,LDH-Iの上昇,心エコーでのhypokinesis,心原性ショックなど"心筋梗塞"を思わせる所見を示した。第5病日に右内頸—後交通動脈分岐部の動脈瘤が再破裂して死亡した。剖検では,肉眼的には冠状動脈の閉塞や心筋の変化を認めないが,光顕では,心筋の特異な変性壊死像(myocytolysis)を認め,視床下部には小出血病変がみられた。くも膜下出血により生じた視床下部病変によって交感神経系が過亢進し,内因性カテコールアミンが多量に放出され,その作用で,全身の末梢血管や冠状動脈およびその末梢の血管れん縮が生じて,肺水腫と心筋障害がひきおこされたと考察した。
A case of subarachnoid hemorrhage complicated by neurogenic pulmonary edema and neurogenic myocardial damage is reported.
A 50-year-old woman was admitted following the sudden onset of headache and disturbance of consciousness due to a ruptured internal carotid posterior comminucating artery aneurysm on the right side. She showed respiratory failure dueto pulmonary edema, which subsequently improved with the mechanical ventilation. After that, she manifested chest distress and hypotensive episode then occurred. An ECG showed QS wave and ST elevation which suggested the presence of infero-lateral myocardial damage. Subsequent rises in serum GOT, GPT, LDH and CPK were noticed. CPK-MB and LDH I and V isozyme levels rose. An echo cardiogram showed hypokinesis of the apical half of the left ventricular septum. The patient died on 5 th hospital day due to rerupture of the cerebral aneurysm. Autopsy revealed diffuse myocytolysis with coagulation necrosis of the heart muscle without occlusion of coronary arteries. A small hemorrhagic lesion was found in the hypo-thalamus. We suggested that a hypothalamic lesion due to subarachnoid hemorrhage stimulated the sympathetic nervous system which in turn dis-charged endogenic catecholamine. This was pro-bably accompanied by vasospasm of the coronary arteries and systemic peripheral arterioles. Fur-thermore, myocardial oxygen consumption could have been increased by the increase in catecho-lamine. Finally, it gave rise to neurogenic pul-monary edema and extensive diffuse myocytolysis of the heart occurred.
Copyright © 1985, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


