Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
はじめに
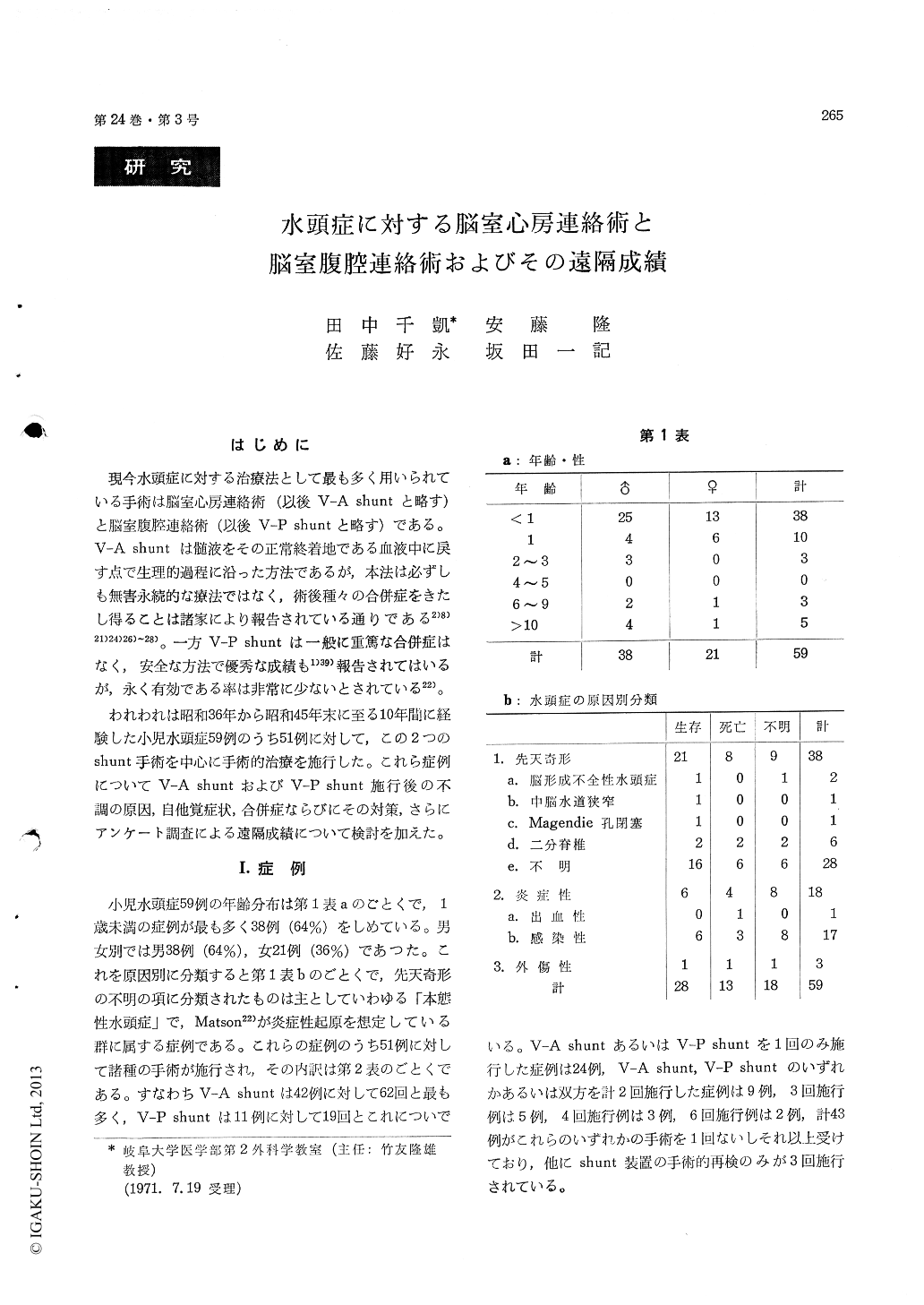
現今水頭症に対する治療法として最も多く用いられている手術は脳室心房連絡術(以後V-A shuntと略す)と脳室腹腔連絡術(以後V-P shuntと略す)である。V-A shuntは髄液をその正常終着地である血液中に戻す点で生理的過程に沿った方法であるが,本法は必ずしも無害永続的な療法ではなく,術後種々の合併症をきたし得ることは諸家により報告されている通りである2)8)21)24)26)〜28)。一方V-P shuntは一般に重篤な合併症はなく,安全な方法で優秀な成績も1)39)報告されてはいるが,永く有効である率は非常に少ないとされている22)。
われわれは昭和36年から昭和45年末に至る10年間に経験した小児水頭症59例のうち51例に対して,この2つのshunt手術を中心に手術的治療を施行した。これら症例についてV-A shuntおよびV-P shunt施行後の不調の原因,自他覚症状,合併症ならびにその対策,さらにアンケート調査による遠隔成績について検討を加えた。
In 51 cases of infantile hydrocephalus, 62 ventri-culoatrial shunt operation (V-A shunt) and 19 ventriculo-peritoneal shunt operation (V-P shunt) were performed, using slit-valve type shunting apparatuses. Postoperative shunt dysfunction was observed in 32 of 62 V-A shunts and in 16 of 19 V-P shunts. Most frequent causes of dysfunction were obstruction of ventricular catheter (16 times or 26%) in V-A shunt and slipping out or obstruc-tion of peritoneal catheter (8 times or 42%) in V-P shunt. As for duration of shunt function V-A shunt was superior to V-P shunt. As postoperative symptoms, fever, vomiting, wound infection and CSF leakage from wounds were observed after V-A shunt, whereas less fever and more CSF leakage cases were observed after V-P shunt. As posto-perative complications, a few severe complications such as meningitis and septicemia were seen after V-A shunt, whereas there was no severe complica-tion after V-P shunt. As for safety, therefore, V-P shunt was superior.
For preventing obstruction of ventricular cathe-ter, combined use of a flat bottom Mishler double lumen reservoir and a Portnoy ventricular cathe-ter was found to be useful. For preventing septi-cemia, not only improved aseptic measure such as routine application of a plastic drape during oper-ation is important, but also determination of optimal cardiac catheter insertion by means of intracardiac electrocardiography with combined use of intra-operative neck flexion (devised by us) is useful for preventing the type of septicemia caused by injury of the tricuspid valve.
An inquiry by enquête on remote status of our cases of hydrocephalus revealed that, of 28 survi-ving cases, 12 (43% of the survivers, 20% of the total cases) were of good prognosis. Prognosis in those cases was also analyzed in relation to pre-operativeCSF pressure, degree of ventricular dilata-tion and head circumference.
Copyright © 1972, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


