Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
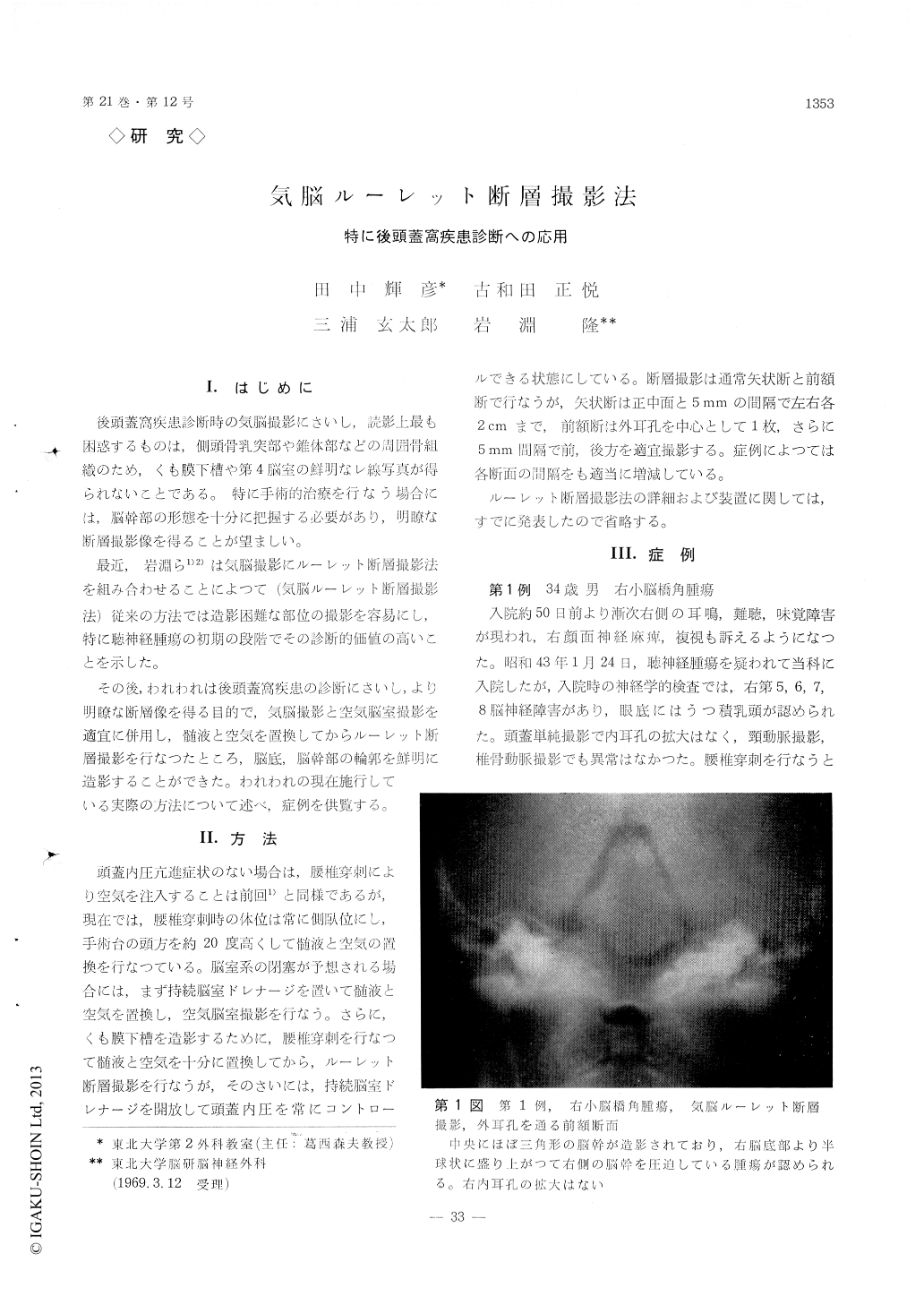
後頭蓋窩疾患診断時の気脳撮影にさいし,読影上最も困惑するものは,側頭骨乳突部や錐体部などの周囲骨組織のため,くも膜下槽や第4脳室の鮮明なレ線写真が得られないことである。特に手術的治療を行なう場合には,脳幹部の形態を十分に把握する必要があり,明瞭な断層撮影像を得ることが望ましい。
最近,岩淵ら1)2)は気脳撮影にルーレット断層撮影法を組み合わせることによつて(気脳ルーレット断層撮影法)従来の方法では造影困難な部位の撮影を容易にし,特に聴神経腫瘍の初期の段階でその診断的価値の高いことを示した。
Pneumoencephalo-roulette tomography combined with pneumoventriculography was found to be of value for the diagnosis of lesions of the suboccipital and skull base region.
Recently, in order to visualize a finer structure without interference from blurring bony shadows, we have performed pneumoencephalography in the pa-tient of increased intracranial pressure following pneumoventriculography, controlling the intracranial pressure through continuous ventricle drainage. In a lateral position, the head and shoulders of the patient was elevated approximately 20 degrees as usual when the cerebrospinal fluid was replaced with air by lumbar puncture. Thus pneumoencephalo-rOulette tomography was performed even in the case of increased intracranial pressure.
Case 1: A 34-year-old man was admitted on Jan. 24, 1968, suffering from the disturbances of the right V, VI, VII, VIII brain nerves of 40 days duration on suspecion of acoustic neurilemmoma. There was, however, no erosion at the right internal auditory meatus in the plain skull roentgenograms. In frontal plane of pneumoencephalo-roulette tomography, a tumor was clearly demonstrated, which grew semiglo-bularly from the skull base and compressed the right brain stem. Operation revealed cancer metastasis from unknown origin at the cerebellopontine angle.
Case 2: This 12-year-old girl was admitted on Sep. 30, 1968, complaining of headache and gait distur-bance. Her neurological findings were disturbances of the left III, V, VII, VIII, IX, X and the right X brain nerves, the right hemiparesis, nystagmus and papilledema. The pneumoventriculogram revealed symmetrical dilatation of both lateral ventricles and postero-superiorly shifted aqueduct of Sylvius, 3rd and 4th ventricles. Lumbar puncture was performed in lateral position, after opening of continuous ven-tricle drainage, and ca 150 ml of fluid was replaced by air uneventfully.
The pneumoencephalo-roulette tomogram demon-strated, in the sagittal plane, irregular enlargement of the ventral portion of the pons. In the frontal plane of the tomogram taken through 5 mm anterior to the center of external auditory meatus, ventral portion of the pons was not visualized on the left side, showing the tumor itself.
Operation revealed the reddish-brown, solid pontine tumor, microscopically astrocytoma grade II.
Case 3: A 11-year-old girl who had been suffered from rheumatic fever 3 years previously, was admitt-ed on Oct. 15, 1968, with complaints of headache and vomiting. Plain skull roentgenogram showed marked digital impressions. The pneumoventriculogram re-vealed symmetrical dilatation of both lateral and 3rd ventricles but the aqueduct of Sylvius was visualized only by its anterior portion. The pneumoencephalo-roulette tomogram, performed after the control of intracranial pressure, demonstrated the 4th ventricle of normal shape and obvious obstruction of the aqueduct of Sylvius at the posterior portion. Inflam-matory obstruction was suspected and ventriculoatrio-stomy was performed.
Case 4: This 6-year-old boy was admitted on Dec. 26, 1968, in stupor with headache, vomiting and the right hemiparesis of 4 days duration. Plain skull roentgenogram showed dilated sella turcica with des-truction of dorsum sellae. The vertebral angiogram showed marked postero-superior displacement of basi-lar artery at the middle and distal part. The triculogram revealed symmetrically dilatated lateral pneumovenventricles and postero-superiorly displaced aqueduct of Sylvius, 3rd and 4th ventricles. The pneumoencephalo-roulette tomogram, in sagittal plane, demonstrated an oval, infant's fist-sized tumor at the skull base, which compressed the 3rd ventricle anterosuperiorly, aqueduct of Sylvius upwards and the 4th ventricle with medulla oblongata postero-superiorly. Operation revealed a cystic craniopharyngioma, about 90 ml of content with cholesterine crystals.
Case 5: A 26-year-old man was admitted on Dec. 9, 1968, suffering from cerebellar ataxia of 6 years duration. He could not stand up-right and walk by himself, nor speak quickly. Finger-to-finger, finger. to-nose and heel-to-knee test proved not to be well done. The pneumoencephalo-roulette tomogram, in sagittal plane, showed normal figure of brain stem but the cerebellum was smaller than usual in shape. The cerebellar gyri were also demonstrated as coral-liform at the superior portion, which was hard to see in the usual tomogram. From these findings cere-bellar atrophy was highly suspected.
Copyright © 1969, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


