Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
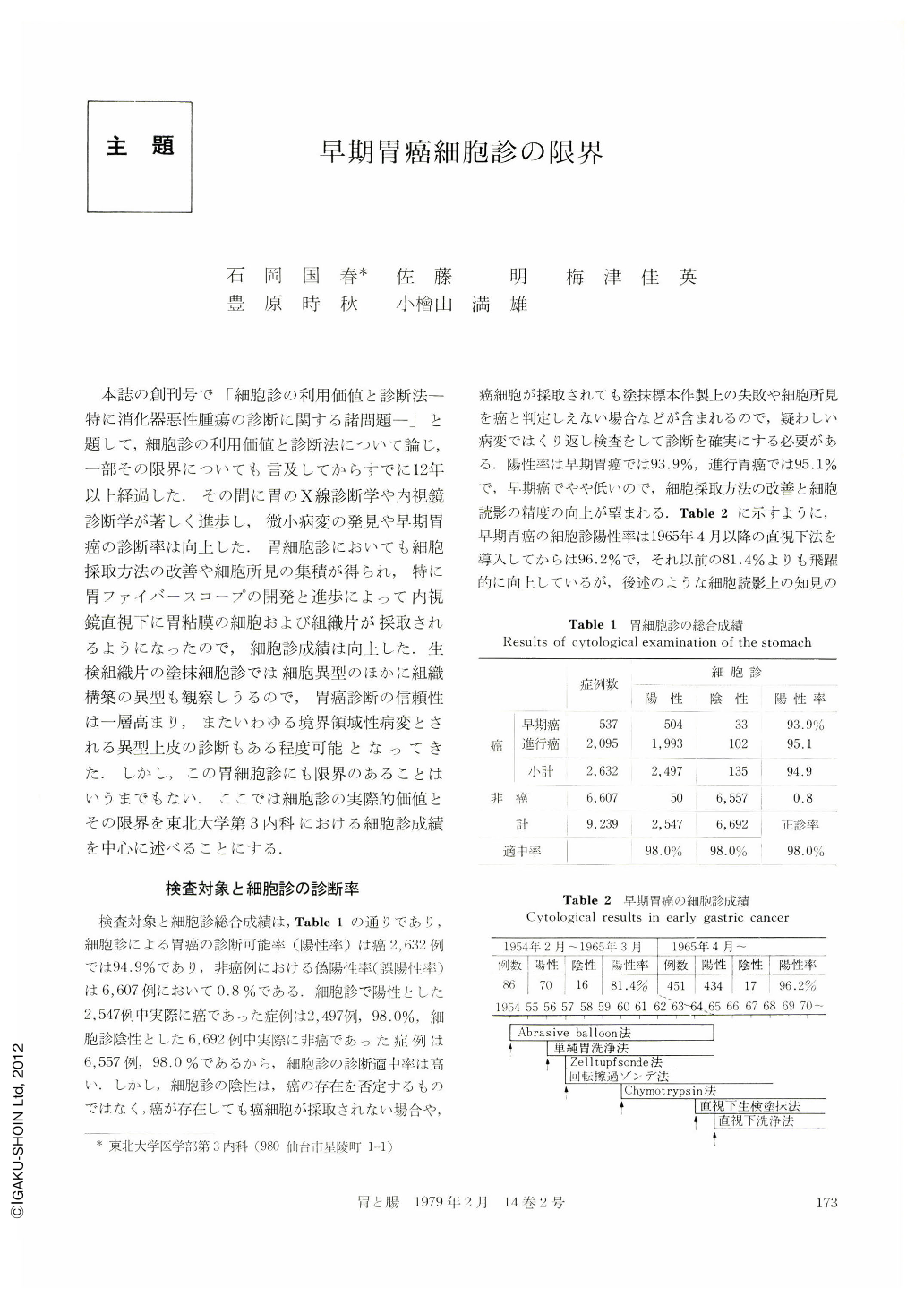
本誌の創刊号で「細胞診の利用価値と診断法-特に消化器悪性腫瘍の診断に関する諸問題-」と題して,細胞診の利用価値と診断法について論じ,一部その限界についても言及してからすでに12年以上経過した.その間に胃のX線診断学や内視鏡診断学が著しく進歩し,微小病変の発見や早期胃癌の診断率は向上した.胃細胞診においても細胞採取方法の改善や細胞所見の集積が得られ,特に胃ファイバースコープの開発と進歩によって内視鏡直視下に胃粘膜の細胞および組織片が採取されるようになったので,細胞診成績は向上した.生検組織片の塗抹細胞診では細胞異型のほかに組織構築の異型も観察しうるので,胃癌診断の信頼性は一層高まり,またいわゆる境界領域性病変とされる異型上皮の診断もある程度可能となってきた.しかし,この胃細胞診にも限界のあることはいうまでもない.ここでは細胞診の実際的価値とその限界を東北大学第3内科における細胞診成績を中心に述べることにする.
We present here practical merits and limitations of cytodiagnosis for early gastric cancer on the basis of our experience.
In patients with gastric cancer the diagnostic accuracy of cytologic findings was seen in 94.9 per cent, while in those with non-cancerous lesions the false-positive rate was 0.8 per cent. The accuracy of cytodiagnosis in patients with positive cytologic findings for cancer was 98 per cent. In patients with early gastric cancer positive cytologic findings were obtained in 93.9 per cent. Since the introduction of cytologic study under direct vision the rate of accurate detection rose up to 96.2 per cent, about a rise of 15 per cent accuracy as compared with the results up to that time, when the positive rate was 81.4 per cent. In patients with early gastric cancer examined in the recent four years the rate of accurate cytodiagnosis was more than 95 per cent, while false-positive rate went down by 0.5 per cent. Evaluation of the diagnostic accuracy of gastric cytology revealed some differences in relation to the histologic types of early cancer. Positive results were slightly lower in the types Ⅰ and Ⅲ. The other types showed a positive rate of more than 95 per cent. In a patient with Ⅱb which was a very small carcinoma less than 1 cm in diameter, cancer cells were detected by gastric washings of the selective site as determined by direct view. Histologic examination of the biopsy specimens in this individual was negative for cancer. Gastric washings were used to better advantage in such a small Ⅱb or other minute carcinomas. The positive rate of cytodiagnosis in 30 patients with minute early cancer less than 1 cm in the greatest diameter was 86.7 per cent, a figure lower than that for early cancer more than 1 cm in diameter. Nonetheless, the final positive rate rose up to 96.7 per cent by the combined use of X-ray, endoscopy, biopsy and cytodiagnosis.
Cancer cells in early carcinoma of the stomach are often less atypical than those in advanced carcinoma. However, since it is now possible to arrive at the correct cytodiagnosis of atypical epithelium by findings of smear materials and also to well differentiate between atypical epithelium and early cancer of differentiated tubular adenocarcinoma, combination of biopsy and cytodiagnosis belongs to the most effective weapons for these lesions. Furthermore, thorny needle biopsy has made it possible to ascertain the histologic background of submucosal tumors of the stomach.
Copyright © 1979, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


