Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
I.はじめに
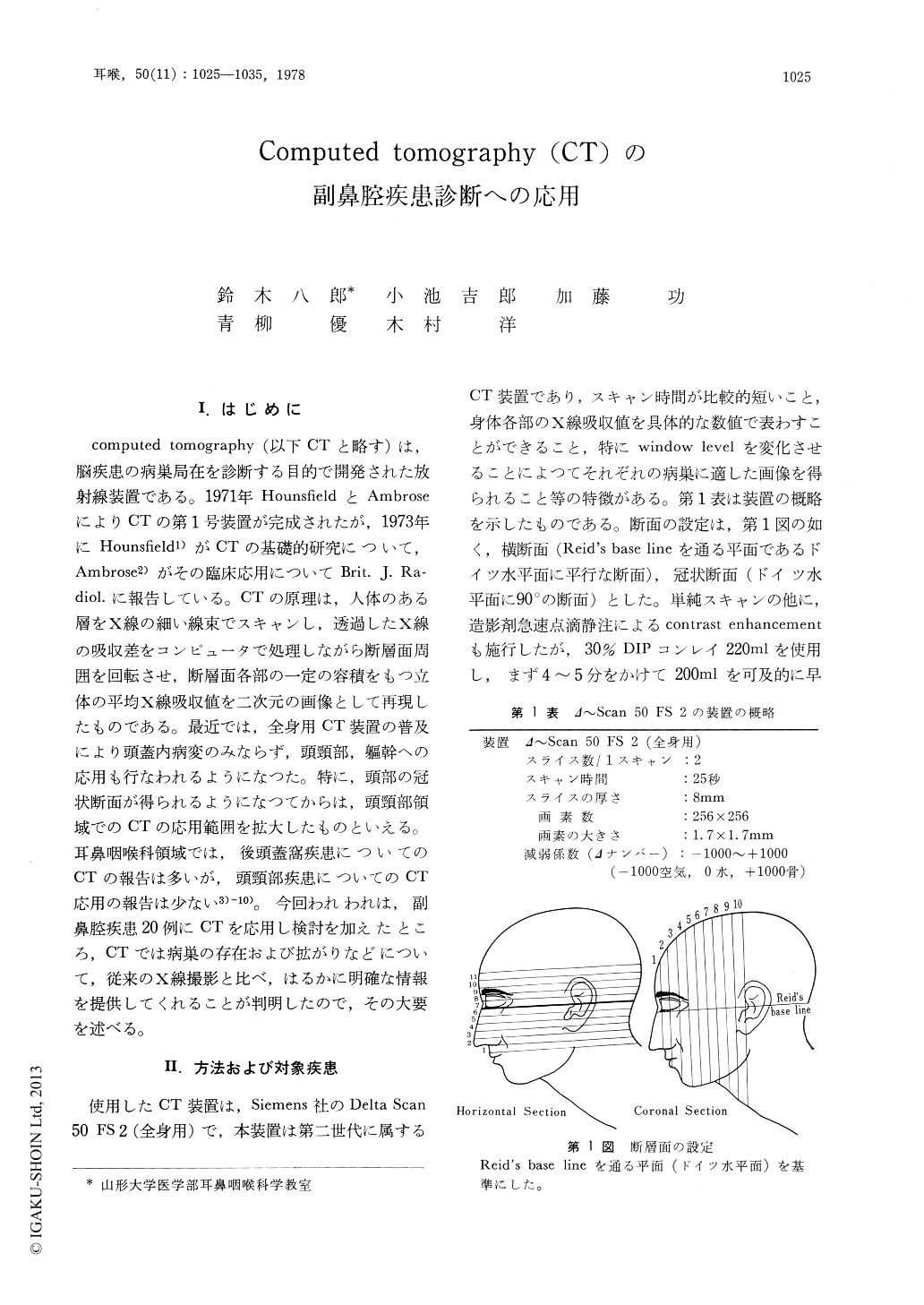
computed tomography(以下CTと略す)は,脳疾患の病巣局在を診断する目的で開発された放射線装置である。1971年HounsfieldとAmbroseによりCTの第1号装置が完成されたが,1973年にHounsfield1)がCTの基礎的研究について,Ambrose2)がその臨床応用についてBrit. J. Radiol. に報告している。CTの原理は,人体のある層をX線の細い線束でスキャンし,透過したX線の吸収差をコンピュータで処理しながら断層面周囲を回転させ,断層面各部の一定の容積をもつ立体の平均X線吸収値を二次元の画像として再現したものである。最近では,全身用CT装置の普及により頭蓋内病変のみならず,頭頸部,躯幹への応用も行なわれるようになつた。特に,頭部の冠状断面が得られるようになつてからは,頭頸部領域でのCTの応用範囲を拡大したものといえる。耳鼻咽喉科領域では,後頭蓋窩疾患についてのCTの報告は多いが,頭頸部疾患についてのCT応用の報告は少ない3)〜10)。今回われわれは,副鼻腔疾患20例にCTを応用し検討を加えたところ,CTでは病巣の存在および拡がりなどについて,従来のX線撮影と比べ,はるかに明確な情報を提供してくれることが判明したので,その大要を述べる。
Twenty patients with the paranasal sinus diseases were evaluated by computed tomography (CT). In our experience, CT has proved completely reliable for detecting a mass in the paranasal sinus, determining the direction and degree of extension of the lesion, and bone destruction in the paranasal sinus and the adjacent bones. Contrast enhancement was found to be of considerable help in differentiation of malignant tumors especially from a cyst of the paranasal sinus with bone destruction.
However, in cases of the poorly developed paranasal sinus, CT was not so reliable to detect a mass in the paranasal sinus.
Copyright © 1978, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


