Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
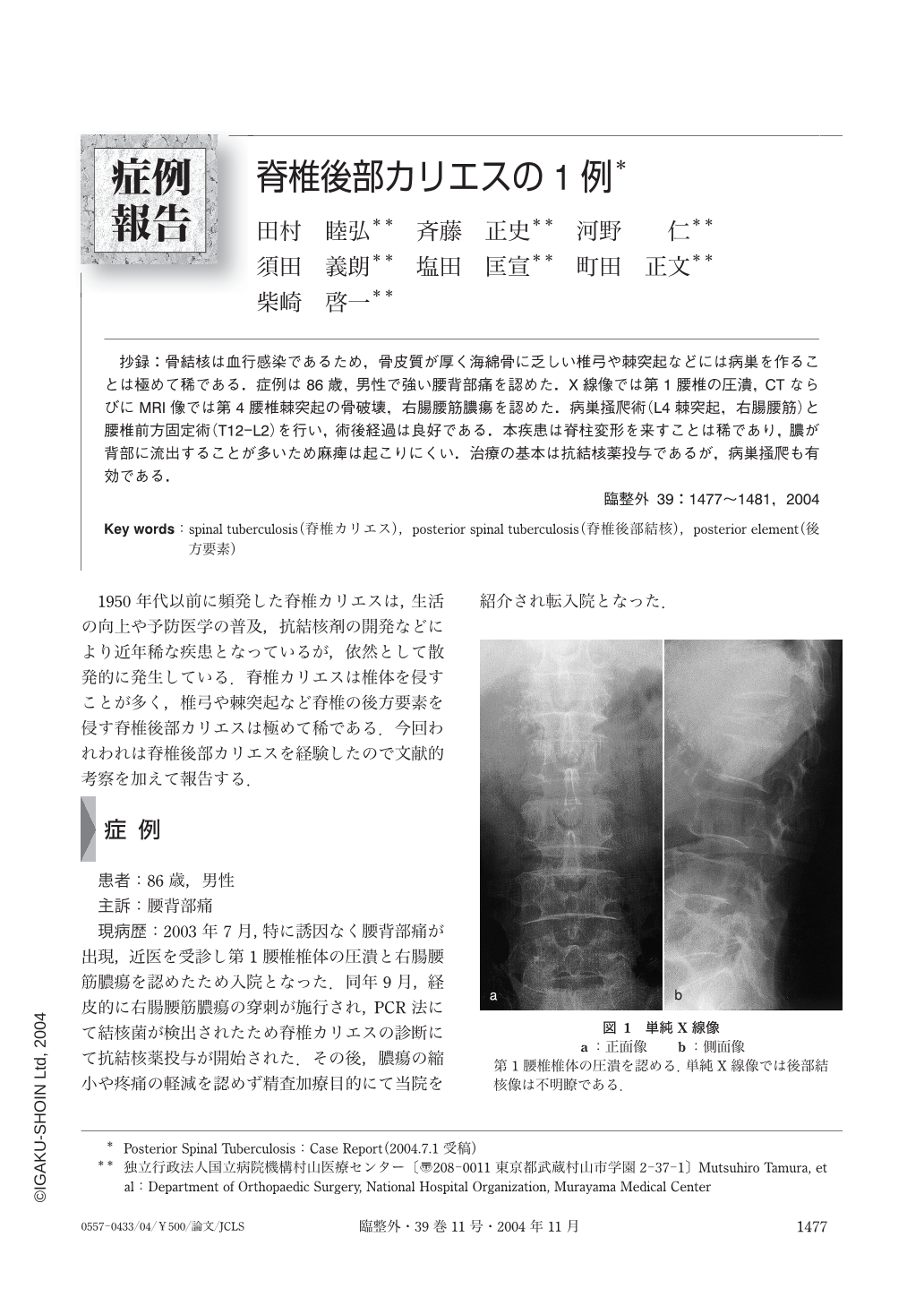
抄録:骨結核は血行感染であるため,骨皮質が厚く海綿骨に乏しい椎弓や棘突起などには病巣を作ることは極めて稀である.症例は86歳,男性で強い腰背部痛を認めた.X線像では第1腰椎の圧潰,CTならびにMRI像では第4腰椎棘突起の骨破壊,右腸腰筋膿瘍を認めた.病巣掻爬術(L4棘突起,右腸腰筋)と腰椎前方固定術(T12-L2)を行い,術後経過は良好である.本疾患は脊柱変形を来すことは稀であり,膿が背部に流出することが多いため麻痺は起こりにくい.治療の基本は抗結核薬投与であるが,病巣掻爬も有効である.
Posterior spinal tuberculosis involving the posterior elements of the spine, including the vertebral arch and spinous processes, is rather rare. We encountered an 86-year-old man with posterior spinal tuberculosis who initially presented with severe back pain. X-ray imaging revealed collapse of the first lumbar vertebra (L1). CT and MRI revealed destruction of the spinous process of L4 and an abscess of the right iliopsoas muscle. Tubercle bacilli were detected in the pus obtained by puncture of the iliopsoas muscle abscess. Anterior fusion of the lumbar spine, bone grafting (T12-L2), and curettage of the lesions (right iliopsoas muscle abscess and L4 spinous process) were performed, and the postoperative course was favorable. Since tuberculosis of bone is caused by hematogenous spread, lesions rarely develop in the posterior part of the spine, where the cortex is thick and cancellous bone is sparse. Posterior spinal tuberculosis rarely leads to spinal deformity. Because the pus frequently escapes posteriorly, paralysis is also rare. MRI is useful in making the diagnosis. Treatment is based on administration of a course of antitubercular drugs and incision and drainage of the lesions.
Copyright © 2004, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


