Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
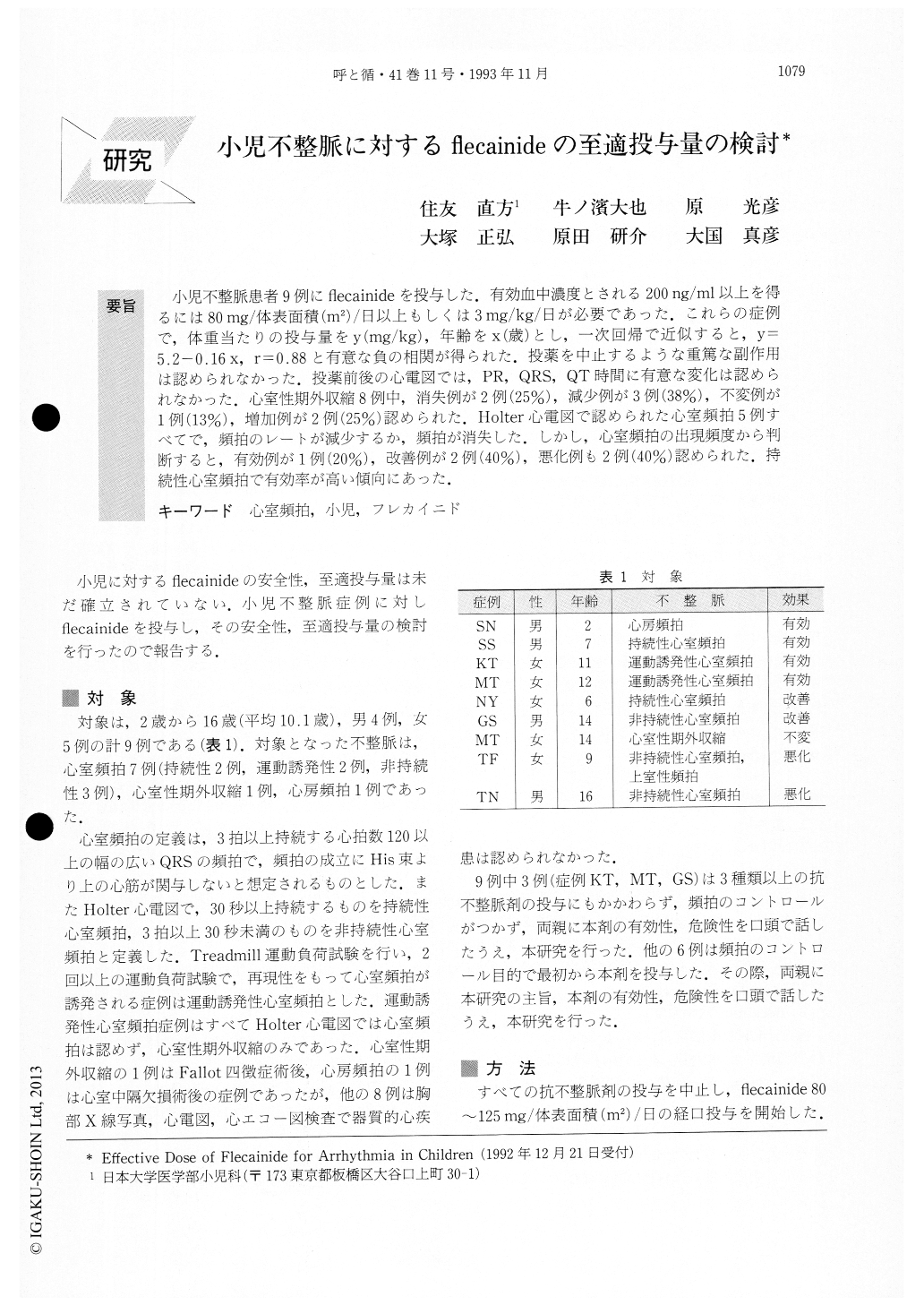
小児不整脈患者9例にflecainideを投与した.有効血中濃度とされる200ng/ml以上を得るには80mg/体表面積(m2)/日以上もしくは3mg/kg/日が必要であった.これらの症例で,体重当たりの投与量をy(mg/kg),年齢をx(歳)とし,一次回帰で近似すると,y=5.2-0.16x,r=0.88と有意な負の相関が得られた.投薬を中止するような重篤な副作用は認められなかった.投薬前後の心電図では,PR,QRS,QT時間に有意な変化は認められなかった.心室性期外収縮8例中,消失例が2例(25%),減少例が3例(38%),不変例が1例(13%),増加例が2例(25%)認められた.Holter心電図で認められた心室頻拍5例すべてで,頻拍のレートが減少するか,頻拍が消失した.しかし,心室頻拍の出現頻度から判断すると,有効例が1例(20%),改善例が2例(40%),悪化例も2例(40%)認められた.持続性心室頻拍で有効率が高い傾向にあった.
Nine children with arrhythmia (1 automatic atrial tachycardia, 1 premature ventricular contruction, and 7 ventricular tachycardia) who started oral treatment using flecainide were studied. All but 2 cases (1 post operative ventricular septal defect, 1 post operative tetralogy of Fallot) had ostensibly normal heart on physical examination, chest X ray and echocardiogram. To raise serum level above 200ng/ml, flecainide dose over 80mg/m2 or 3mg/kg was needed. There was negative correlation between dose (y : mg/kg) and age (x: year) (y=5.2-0.16x, r=0.88) in this group.
Copyright © 1993, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


