Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
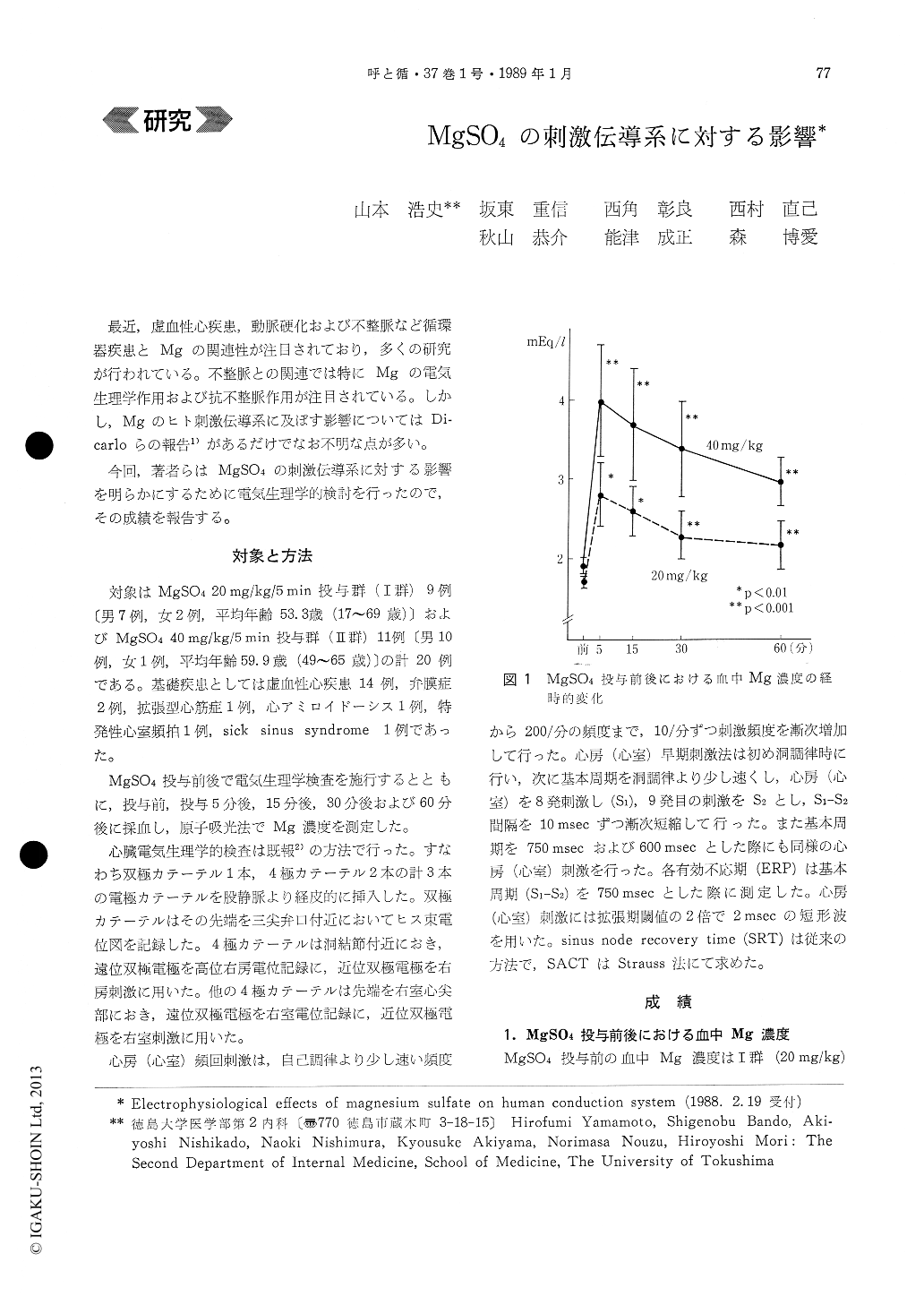
最近,虚血性心疾患,動脈硬化および不整脈など循環器疾患とMgの関連性が注目されており,多くの研究が行われている。不整脈との関連では特にMgの電気生理学作用および抗不整脈作用が注目されている。しかし,Mgのヒト刺激伝導系に及ぼす影響についてはDi—carloらの報告1)があるだけでなお不明な点が多い。
今回,著者らはMgSO4の刺激伝導系に対する影響を明らかにするために電気生理学的検討を行ったので,その成績を報告する。
Electrophysiological studies were performed to evaluate the effects of MgSO4 on human conduction system. Nine patients who received 20 mg/kg of MgSO4 did not show any significant changes in the electrophysiological parameters except for prolonga-tions in the PR and AH intervals. After the infu-sion of 40 mg/kg of MgSO4 in eleven patients, sinus cycle length and corrected sinus node recovery time were increased but statistically insignificantly. Sinoat-rial conduction time, the PR interval and AH inter-val were increased. The effective refractory period (ERP) of right atrium, ERP of atrioventricular node (AV node), ERP of right ventricule and ERP/QTc were increased significantly.
These findings suggests that the antiarrhythmic effects of magnesium were due to ( 1 ) suppresion of the functions of the sinus and AV nodes, and ( 2 ) shortening of the duration of the ventricular vulne-rable period during the cardiac cycle and prevention of ventricular arrhythmias related reentry mecha-nism.
Copyright © 1989, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


