Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
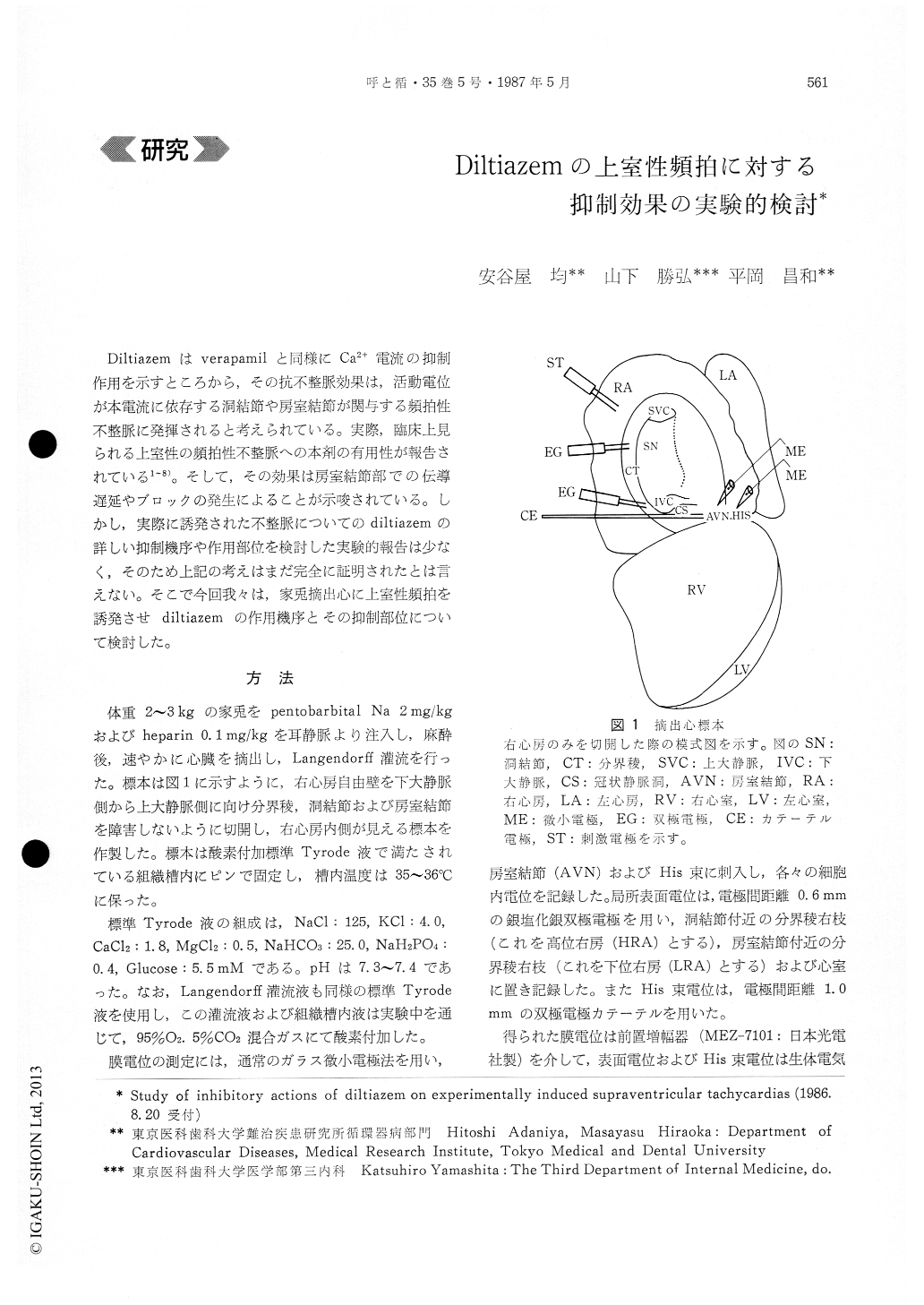
Diltiazemはverapamilと同様にCa2+電流の抑制作用を示すところから,その抗不整脈効果は,活動電位が本電流に依存する洞結節や房室結節が関与する頻拍性不整脈に発揮されると考えられている。実際,臨床上見られる上室性の頻拍性不整脈への本剤の有用性が報告されている1〜8)。そして,その効果は房室結節部での伝導遅延やブロックの発生によることが示唆されている。しかし,実際に誘発された不整脈についてのdiltiazemの詳しい抑制機序や作用部位を検討した実験的報告は少なく,そのため上記の考えはまだ完全に証明されたとは言えない。そこで今回我々は,家兎摘出心に上室性頻拍を誘発させdiltiazemの作用機序とその抑制部位について検討した。
Effects of diltiazem on supraventricular tachycar-dias were studied by the surface electrogram and the microelectrode technique using the isolated rabbit heart under the Langendorf Perfusion. Supraven-tricular tachycardias were induced by applying extra stimuli. Eight among 28 preparations developed supraventricular tachycardias with a mean atrial rate for 310/min with a sudden prologation of A-H interval in response to extra stimuli, while four hearts showed atrial tachycardias (rate: 552/min) without the A-H prolongation or block. The former appeared to be A-V nodal reentry and the latter intraatrial reentry as their mechanisms. The former was abolished by the application of 2x10-6M diltiazem, which caused a conduction block between low right atrium and AV node. Diltiazem did not inhibit the latter type of tachycardia, but it caused a decrease in the ventricular rate by 23%.
Copyright © 1987, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


