Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
- 参考文献 Reference
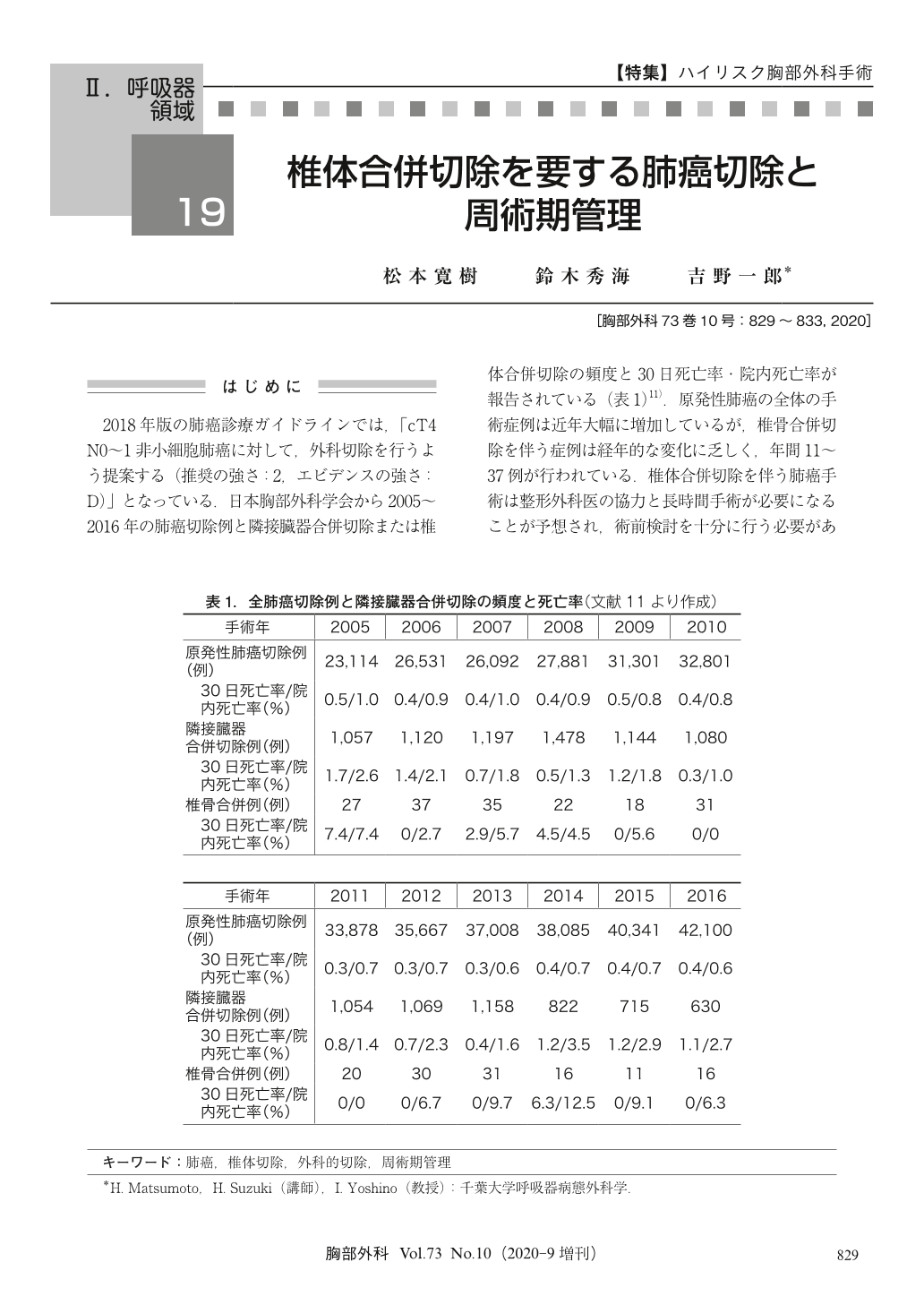
2018年版の肺癌診療ガイドラインでは,「cT4N0~1非小細胞肺癌に対して,外科切除を行うよう提案する(推奨の強さ:2,エビデンスの強さ:D)」となっている.日本胸部外科学会から2005~2016年の肺癌切除例と隣接臓器合併切除または椎体合併切除の頻度と30日死亡率・院内死亡率が報告されている(表1)11).原発性肺癌の全体の手術症例は近年大幅に増加しているが,椎骨合併切除を伴う症例は経年的な変化に乏しく,年間11~37例が行われている.椎体合併切除を伴う肺癌手術は整形外科医の協力と長時間手術が必要になることが予想され,術前検討を十分に行う必要がある.当院での経験をふまえて椎体合併切除を要する肺癌手術の概要について述べる.
While cases of surgical resection for primary lung cancers are increasing, lung cancer requiring vertebrectomy is rare. A high complication rate and recurrence rate have been reported after surgical resection for lung cancer with vertebral invasion. However, select patients who achieve complete resection after effective preoperative chemoradiotherapy show a better survival rate than others. Preoperative computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are necessary to consider surgical strategies and how to resect and reconstruct the vertebral body and chest wall with a clear margin before surgery. A 3-dimensional imaging or simulation model is useful for such ends. Several surgical approaches have been developed, such as the transmanubrial, posterior, posterolateral, or the combination thereof. Proper vertebrectomy (total, hemi, part of a vertebra, or only the transverse process of a vertebra) and reconstruction approaches should be decided in conjunction with orthopedic surgeons. While evidence is lacking, establishing proper surgical indications and developing effective strategies to achieve complete resection with a clear margin are the most critical points in lung cancer requiring vertebrectomy.
© Nankodo Co., Ltd., 2020


