Symposium on Permeability of Biological Membranes
Uncoupling of Na Secretion from K Uptake by DNP in the Sartorius Muscle of Toads
Masayasu Sato
1
,
Sakie Kiyosuke
1
,
Toyoko Wada
1
1Department of Physiology, Kumamoto University Medical School
pp.78-82
発行日 1962年4月15日
Published Date 1962/4/15
DOI https://doi.org/10.11477/mf.2425906228
- 有料閲覧
- 文献概要
- 1ページ目
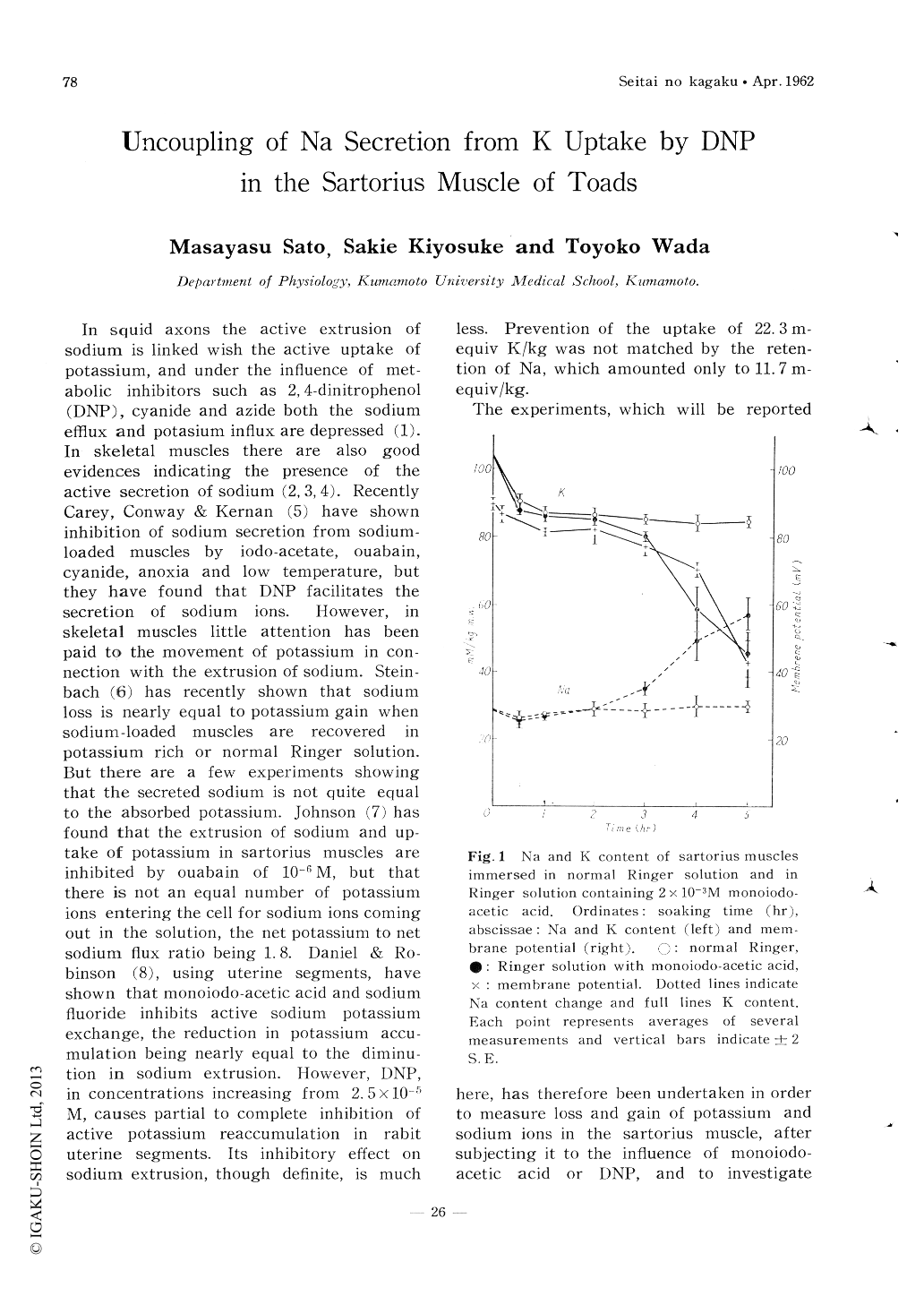
1.Sodium and potassium content of the sartorius muscle of toads was measured after subjecting it to the influence of monoiodoacetic acid or DNP.
2.The muscle poisoned with monoiodoacetic acid shows accumulation of sodium and loss of potassium, both sodium gain and potassium loss being equal.
3.DNP, when its concentration is low or when the temperature is low, first facilitates sodium extrusion, and, with a sufficient concentration and temperature of 25℃,it inhibits sodium extrusion, although the inhibition of sodium extrusion is much less than that of potassium uptake.
4.In DNP-poisoned muscle the oxygen uptake, measured at 25℃,is increased without accompanying an increase in sodium extrusion.
Copyright © 1962, THE ICHIRO KANEHARA FOUNDATION. All rights reserved.


