Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
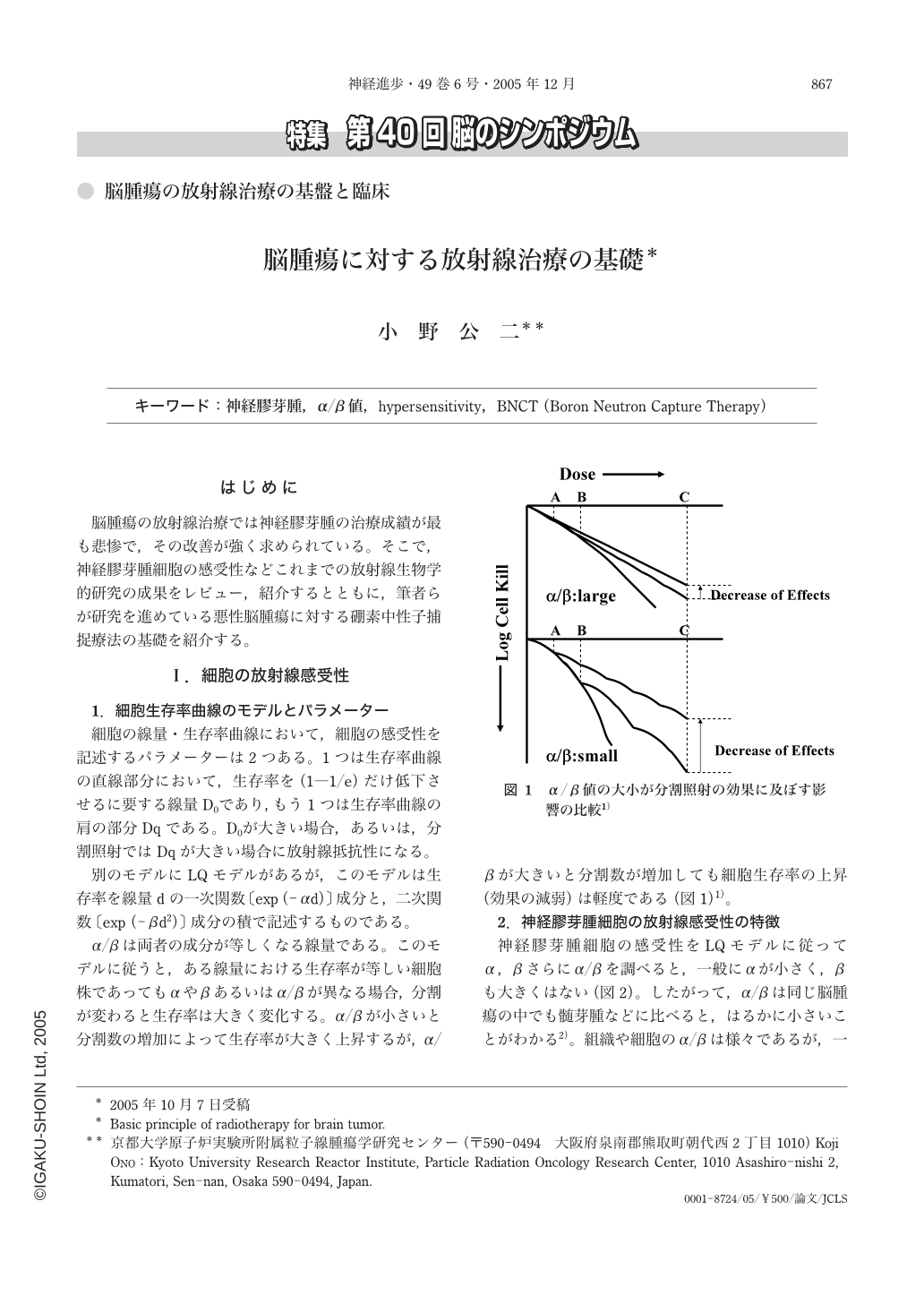
脳腫瘍の放射線治療では神経膠芽腫の治療成績が最も悲惨で,その改善が強く求められている。そこで,神経膠芽腫細胞の感受性などこれまでの放射線生物学的研究の成果をレビュー,紹介するとともに,筆者らが研究を進めている悪性脳腫瘍に対する硼素中性子捕捉療法の基礎を紹介する。
Dose cell survival curve of glioblastoma has following features, i.e., large Dq or small α and α/β values. Dose effect relationship of CNS has also small α/β value, and an increase of fractionation of total dose does not generate therapeutic benefits. Recent research found the phenomenon of hypersensitivity that appeared in the dose of under 0.5 Gy. This is applied to radiotherapy for glioblastoma. On the other hand, a following response of CNS is also recognized that an increase in tolerance dose of CNS by an increase in fractionation of total dose is much less than expectation from LQ model. Boron neutron capture therapy(BNCT), that delivers high LET α particle with short range to tumor cell selectively, is an attractive modality to overcome above difficulties all at once. It is possible to give over 10 times dose of radiation to tumor cells in comparison with co-existing normal cells by combining BPA, tumor seeking boron compound, and slow neutrons. Rapid shrinkage of enhanced lesion in MRI was observed within 48 hours after BNCT. That rapid response is never experienced in regular X-ray therapy.
Copyright © 2005, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


