Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
聾学校生徒を対象に標準12誘導心電図およびホルター心電図を記録し,①先天性聾唖生徒とQT延長発現に関する疫学調査,②不整脈の発生頻度,③先天性聾唖を有する症例でのQT時間,心拍数の日内変動を調べ,若干の知見を得たので報告する。
Clinical investigation was performed on a total of one hundred eleven deaf-mute children aged 5 to 22, using the standard 12-lead ECG and from this group on 24 boys and girls from schools for deaf-mutes in IWATE prefecture the Holier ECG was used.
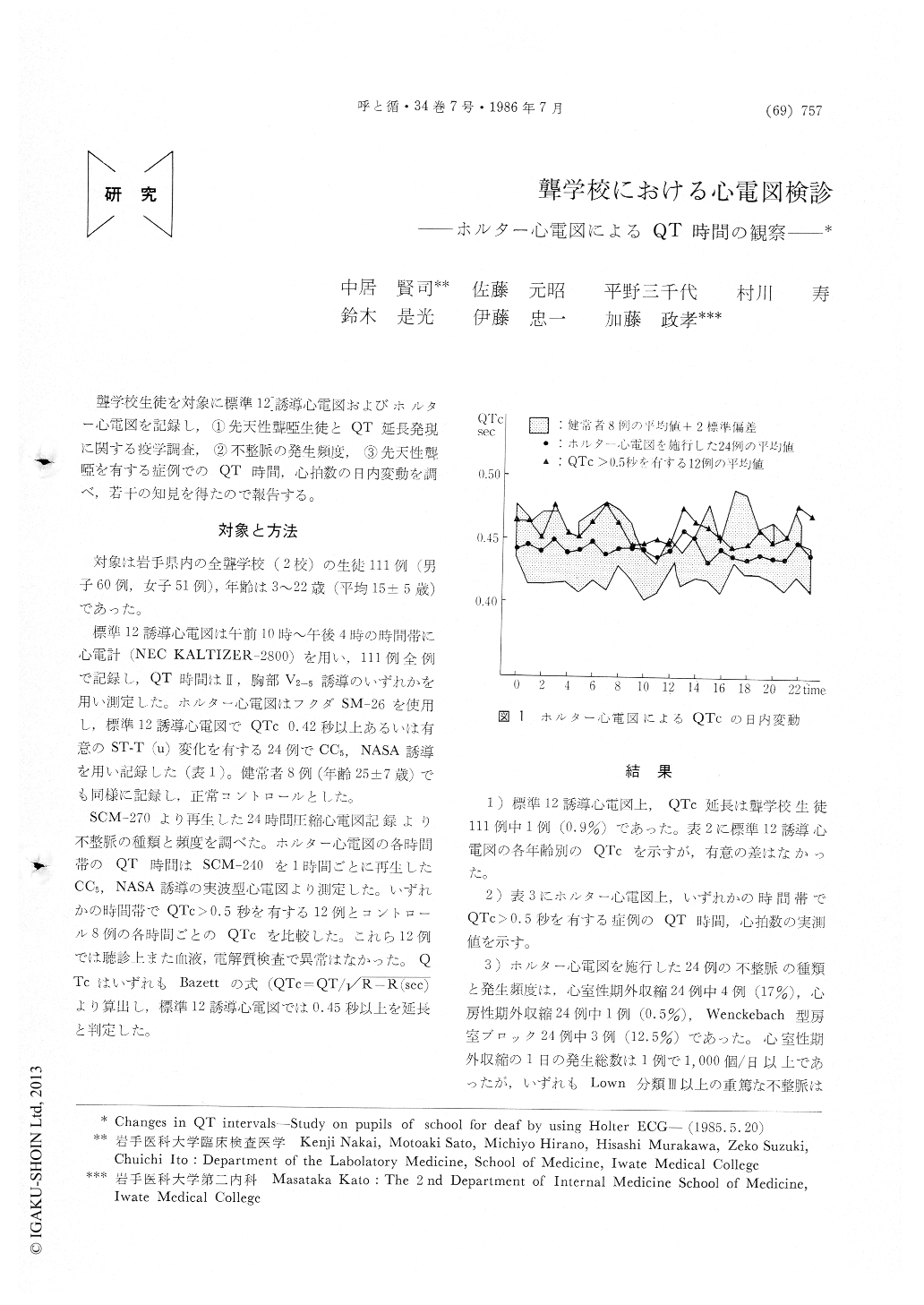
A corrected QT interval (QTc), as calculated using Bazett's formula, was compared with that of 8 healthy young men every 24 hours. A prolonged QT interval (QTc:0.587) on the standard 12-lead ECG occurred one out of the 111 deaf-mute children (0.9 percent), although this 17 year-old deaf-mute school girl had previously no syncopal attack.
Second degree (Wenckebach type) atrioventricular block occurred in 12.5 percent (3/24). Premature beats were always single, atrial in 0.5 percent (1/24), ventricular in 26 percent (6/24). There were no epi-sodes of ventricular or supra-ventricular tachycardia on Holter ECG recording. The value (mean+2 stan-dard deviation) of the most lengthening QTc interval on Holter ECG recording in 8 healthy young men is 0.488 sec at the time 17 : 00. We supposed that the value of QT interval over 0.5 sec on the Holter ECG recording would be prolonged. A lengthening of the QTc interval over 0.5 sec on the Holier ECG recording, as shown in 12 deaf-mute cbildren, occurred mainly at the time 3 : 00, 6 : 00, 13 : 00 and 23 : 00. This was very interesting in considering the pathoge-nesis of a lengthening of the QT interval.
Copyright © 1986, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


