Japanese
English
- 有料閲覧
- Abstract 文献概要
- 1ページ目 Look Inside
典型的な肛門部病変を伴った肉芽腫性大腸炎(大腸クローン病)の1例を経験し,現在まで3年余に亘って臨床的,病理組織学的に経過を観察し得たので報告する.
症例
患 者:25歳 女性 店員 独身
主 訴:粘血便,貧血
家族歴:特記することなし.
既往歴:慢性便秘,高度の蝕歯,扁桃腺炎による発熱多し,虫垂炎の既往なし.
現病歴:20歳頃より紙に着く程度の無痛性肛門出血あり,その頃から便秘がなくなり,1日2回位排便がみられるようになった.
昭和46年1月頃から腹鳴,便意頻回,肛門より粘血性の分泌物をみるようになった.
肛門の外縁に無痛性疣状凹凸を触れるようになったので,某外科を受診し痔核の診断を受けた.同年12月,粘血便の回数が増加すると共に,食欲不振,全身倦怠,顔面蒼白,心気亢進,眩暈,四肢の浮腫を訴えるようになった.続いて四肢に紫斑が現われ,頸部および前胸部に瘙痒感なき湿疹状皮膚変化を認めた.
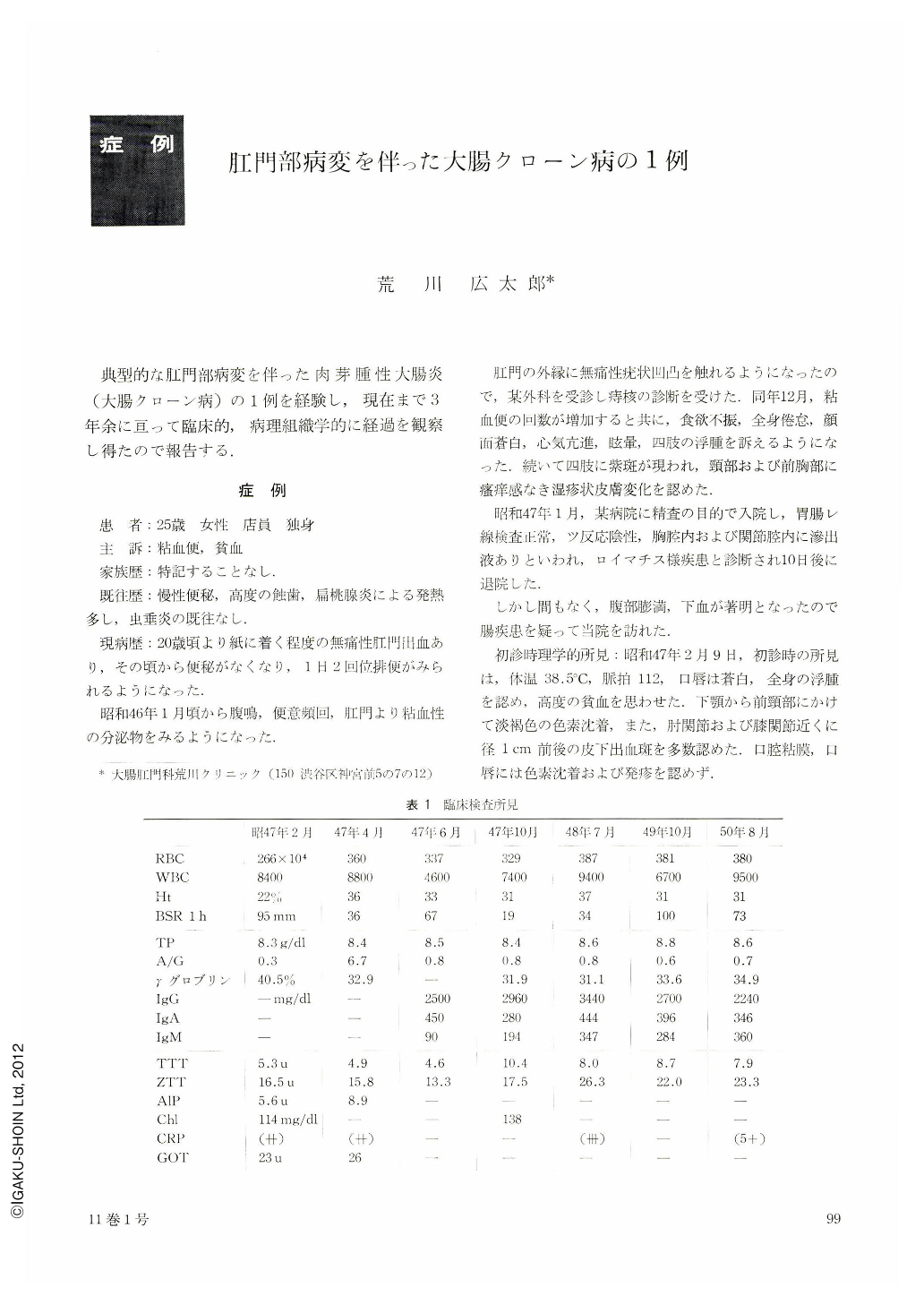
昭和47年1月,某病院に精査の目的で入院し,胃腸レ線検査正常,ツ反応陰性,胸腔内および関節腔内に滲出液ありといわれ,ロイマチス様疾患と診断され10日後に退院した.
しかし間もなく,腹部膨満,下血が著明となったので腸疾患を疑って当院を訪れた.
初診時理学的所見:昭和47年2月9日,初診時の所見は,体温38.5℃,脈拍112,口唇は蒼白,全身の浮腫を認め,高度の貧血を思わせた.下顎から前頸部にかけて淡褐色の色素沈着,また,肘関節および膝関節近くに径1cm前後の皮下出血斑を多数認めた.口腔粘膜,口唇には色素沈着および発疹を認めず.
歯牙はきわめて不良で,ほとんど全歯が蝕歯で末治療の状態にあり,とくに両下顎臼歯は根部を残して消失していた.口蓋扁桃は中等度に肥大していたが,発赤白苔なし.
胸部聴打診では,とくに湿性ラ音なし,濁音界の異常も認められず,胸膜炎を思わせる所見なし.腹部はやや鼓腸を認めるが,腹水を触知せず,右季肋部に肝辺縁二横指を触れる,圧痛なし.
リンパ節は両ソケイ部に小指頭大の硬結を触れる以外は,とくに全身性のリンパ節腫張を認めず.
Anorectal lesions accompanied by granulomatous colitis are well documented by Lockhart-Mammery and Atwell et al., and increasing of cases and the difficulty of their treatments have been pointed out in every medical meeting in the western countries. On the other hand, no typical case has been reported so far in Japan.
This is a report of a case 22 years old female, with Crohn's disease involing the colon and anorectal region. Since 1973 she has been treated and observed both clinically and histopathologically for three years.
The chief complaints were anemia and mucosanguineous stool. Edematous perianal skin tags, reddish blue discoloration of the surrounding skin, and multiple longitudinal deep ulcerations continuous upwards into the rectum were characteristic. Sigmoidscopic examination revealed a stricture of the rectal ampulla surrounded by irregular nodular firm masses, with multiple deep ulcerations therein.
Barium enema X-ray examination showed that irregular nodular lesions looking like cobble stones spread from the anal canal up to the sigmoid colon. Intramucosal lymphoid hyperplasia was also observed in the rest of the colon. Some irregularity of the haustral relief was found in the ileocecal region.
Blood chemistry disclosed a high serum total protein and low A/G ratio, sever anemia, and markedly increased gamma globulin and immunoglobulins.
The patient has been treated on steroid hormone, azathioprine, salazopyrine and antibiotics for the past three years. Her general condition is now satisfactory in spite of the localized ulceration in the rectum, so that she feels well and is working at a department store. Occasional mucosanguineous discharge is the only complaint, without any serious complication.
Histopathological examination of the specimens obtained from the perianal skin, rectal mucosa and inguinal lymphnode led us to a diagnosis of Crohn's disease, because of typical non-caseating giant cell granuloma in each specimen as pointed by Dr. Morson.
Copyright © 1976, Igaku-Shoin Ltd. All rights reserved.


